A Beginner’s Guide to Extrusion
What is extrusion manufacturing and how does it work? Well, extrusion is a process that has been used for centuries. This manufacturing process has been used to make all kinds of products, from aluminum cans to plastic pipes. Extrusions is a manufacturing technique that creates objects with a fixed cross-sectional profile. It does this by forcing material through a die with the desired shape.
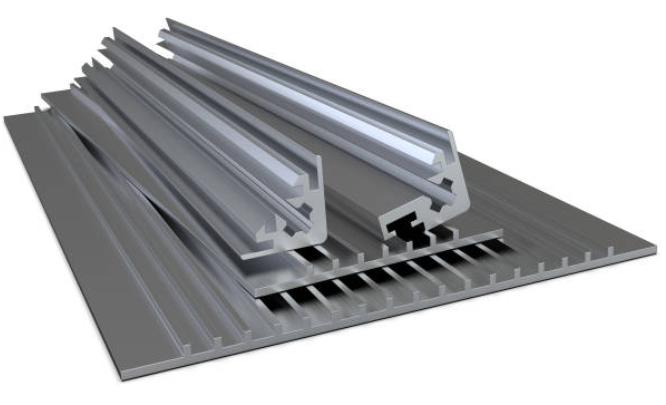

If you’re new to the manufacturing industry, don’t worry, we’ve got you covered! In this article, we’ll explain what extrusion is and how it works.
How many types of extrusion are there?
First things first, let’s talk about the different types of extrusions. There are four main types of extrusion: direct extrusion, indirect extrusion, impact extrusion, and hydrostatic extrusion. Even though each process might vary slightly, the extrusion process involves a billet being pushed through the die opening using a pressing stem (ram) and dummy block.
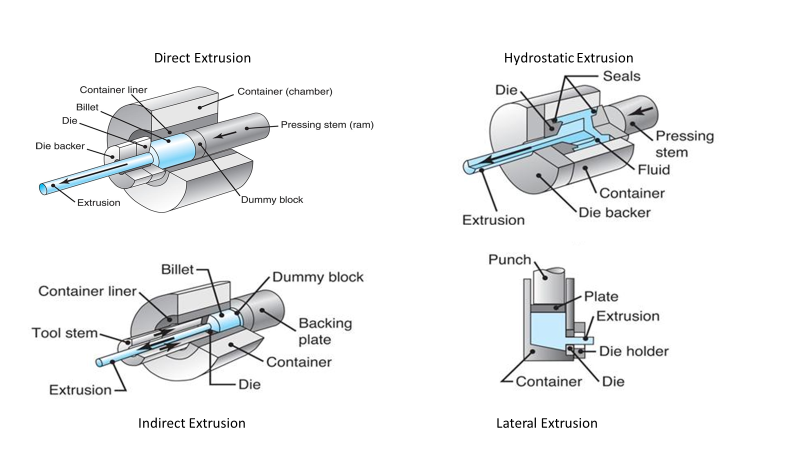
What is an example of extrusion?
An example of products that have been extruded is aluminum cans. In this process, a cylindrical billet of aluminum is heated to a specific temperature and then forced through a die to create a can with a uniform cross-sectional profile. This method is also used to manufacture a variety of other products, such as pasta, pipes, window panes, gears, snack foods, railings, shower stalls, and windshield wipers, all of which are formed by extruding material through a die to achieve a specific shape.
What is direct extrusion used for?
Direct extrusion is a type of extrusion process that involves pushing a heated metal billet through a die. Direct extrusion is used for a wide range of applications. This process can manufacture simple shapes like rods and tubes to more complex profiles like those used in the construction, automotive, and aerospace industries. Some of the key advantages of direct extrusion include:
- High production rates: Direct extrusion can produce parts at a high rate of speed, making it a cost-effective way to manufacture large quantities of parts.
- Tight tolerances: Direct extrusion can produce parts with tight tolerances and precise dimensions, making it an ideal process for creating complex shapes and profiles.
- Minimal waste: Direct extrusion produces very little waste, as the metal is simply pushed through the die and shaped into the desired profile.
Some specific examples of parts and products that can be manufactured using direct extrusion include:
- Aluminum extrusions for window frames, door frames, and other building components
- Automotive parts like chassis components, heat exchangers, and engine components
- Aerospace components like structural components and landing gear components

What is shape extrusion?
Shape extrusion is a type of extrusion process that involves pushing a heated metal billet through a shaped die to create a specific shape or profile. Unlike direct extrusion, which typically produces simple shapes, shape extrusion is used to produce more complex shapes with varying cross-sectional geometries. A billet is then pushed through a shaped die, which gives the metal its final form.

Some of the key advantages of shape extrusion include:
- Precision and complexity: Shape extrusion can produce parts with high precision and complex shapes, allowing manufacturers to create customized parts for specific applications.
- Reduced waste: Shape extrusion produces very little waste, as the metal is shaped directly into the desired form.
- Cost-effective: Shape extrusion can be a cost-effective way to produce complex shapes and profiles, as it can be used with a wide range of metals and can produce parts at high rates of speed.
What types of shapes are extruded?
Some of the most common shapes that metals and metal alloys can be extruded into using shape extrusion include:
- Hollow and solid profiles: Shape extrusion can be used to produce both hollow and solid profiles, such as round or oval tube shapes and hollow square tube shapes.
- Channels and tubes: Shape extrusion is often used to produce tubes and channels with complex cross-sectional geometries, such as Zee or Z-shaped channels.
- T-sections and I-beams: Shape extrusion can also be used to produce Tee or T shapes, H or I beam shapes, L shapes, and other structural shapes that are commonly used in construction and engineering applications.

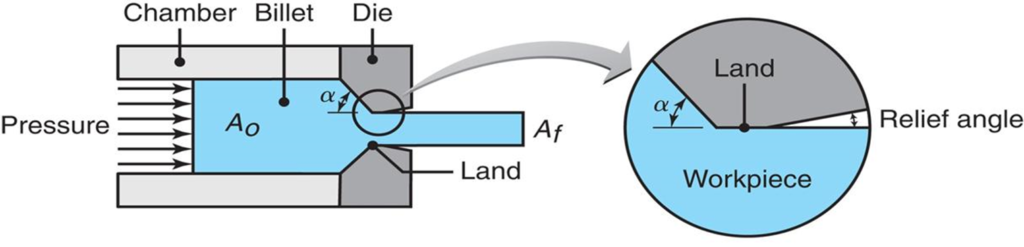
What are the process variables of extrusion?
The three most important process variables that affect the extrusion process, include melt temperature (T), motor load (I), and melt pressure (P). However each of these can be affected by other factors, for example, the extrusion pressure can be affected by the die angle, reduction in cross-section of the material, extrusion speed, and lubrication. As a result, all these variables must be carefully controlled to ensure that the final product meets the required specifications. When the extruder is not functioning correctly one, two, or all three of the process variables could be the problem.
How does temperature affect extrusion?
While extruding materials temperature plays a crucial role. The material must be heated to a specific temperature to soften it enough to flow through the die. If the temperature is too low, the material will not flow properly, and if it is too high, it could cause defects in the final product. It is also important to remember that the deformation energy is converted into heat, thereby increasing the temperature of the extrudate and in turn affecting the microstructure and mechanical properties of the material.
How does metal flow in the extrusion process?
Metal flows through the die in a process called deformation which is a result of the force being applied to the metal to push it through a die. As the metal is pushed through the die, it is compressed and elongated, causing it to take on the shape of the die. The metal endures compressive and shear stress to achieve the die shape. If there is too much friction during the extrusion process, the metal will not flow properly resulting in a dead zone where you have stagnate metal that is not flowing. Below are the types of metal flow that can be experienced while extruding with square dies.
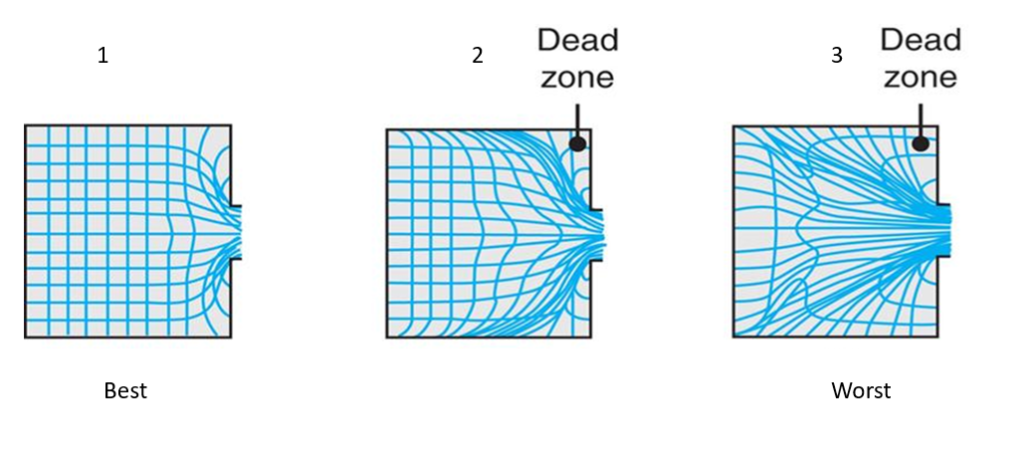
- Flow pattern obtained at low friction or in indirect extrusion.
- The pattern was obtained with high friction at the billet–chamber interfaces.
- The pattern obtained at high friction or with cooling of the outer regions of the hot billet in the chamber; this type of pattern, observed in metals whose strength increases rapidly with decreasing temperature, leads to a defect known as pipe (or extrusion) defect.
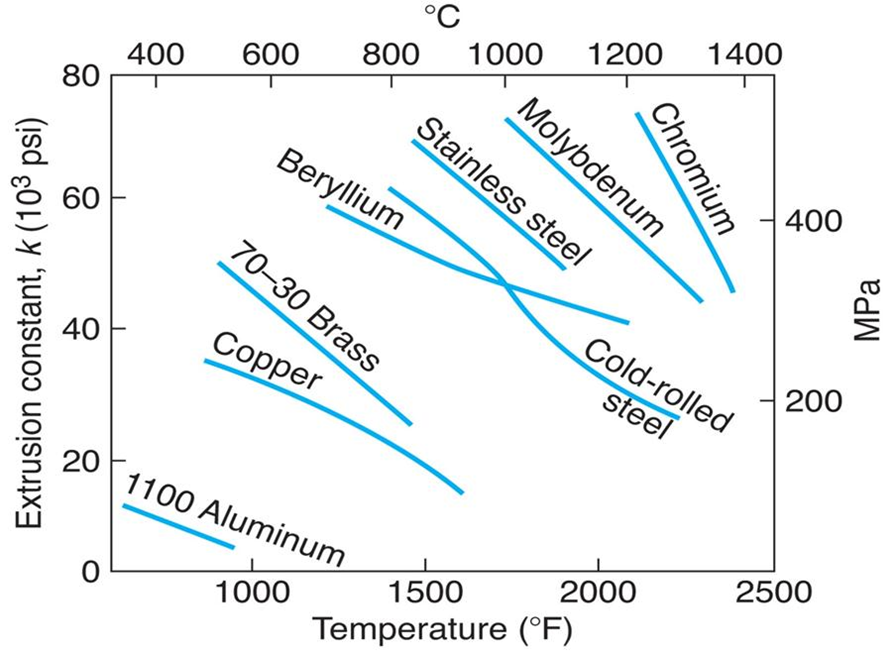
What is the usual temperature range of various metals for hot extrusion?
Aluminum is the most common hot extruded metal, the typical extrusion temperatures range from 700° to 890° Fahrenheit, or 375° to 475° Celsius. See the chart below for extrusion temperature ranges for various materials.

What are the types of dies used for extrusion?
There are several types of dies used for extrusion, including flat-face dies, pocket dies, and feeder dies. The type of die used depends on the shape of the final product.
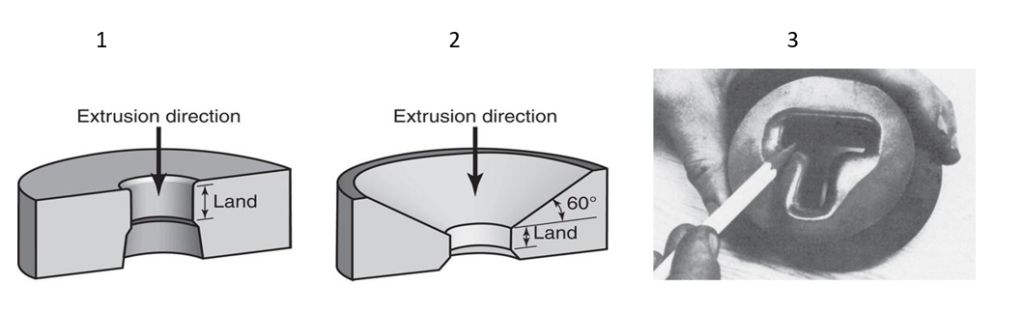
- Flat-face dies: die for nonferrous metals
- Pocket dies: die for ferrous metals
- Feeder dies: die for a shaped extrusion typically made of hot-work die steel and used with molten glass as a lubricant
How is the aluminum tube extruded?
There are two ways to manufacture a seamless aluminum tube direct and indirect, both require a powerful ram to push the aluminum alloy material through a die with a specific tube cross-sectional profile.
- Direct Extrusion: uses an internal mandrel that moves independently of the ram
- Indirect Extrusion: has the mandrel integral with the ram and uses a spider die to produce seamless tubing.

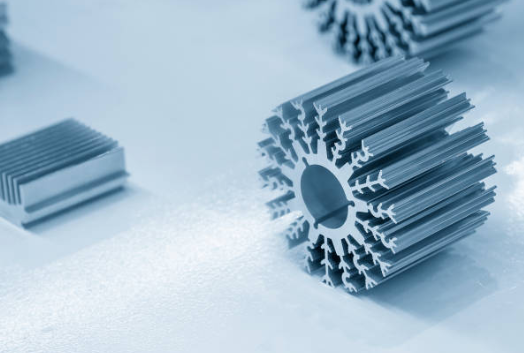
What is an extruded heat sink?
An extruded heat sink is a type of heat sink that is made using the extrusion process. It is used to dissipate heat (thermal management) from electronic components on printed circuit boards. Heat sinks are commonly found in computers and other electronic devices. The most common aluminum alloy is 6063-T5.

What is an example of cold extrusion?
Cold extrusion is a process that involves deforming metal at room temperature. This process is often used to manufacture parts that require high strength and durability. The process can be used with a variety of metals, including aluminum, lead, tin, brass, and steel. Cold extrusion is commonly used to manufacture a wide range of, high-strength parts. Some examples of cold extruded parts are rivets, bolts, screws, fasteners, collapsible tubes, fire extinguisher cases, shock absorber cylinders, spark plugs, and gear blanks.

What do you mean by impact extrusion?
Impact extrusion is a type of extrusion manufacturing process that involves deforming a metal slug using a high-velocity impact to force the material into a die or mold with a punch. This process is commonly used to manufacture parts that require high precision and strength. Some examples of this process are aluminum cans, tubes, and containers.
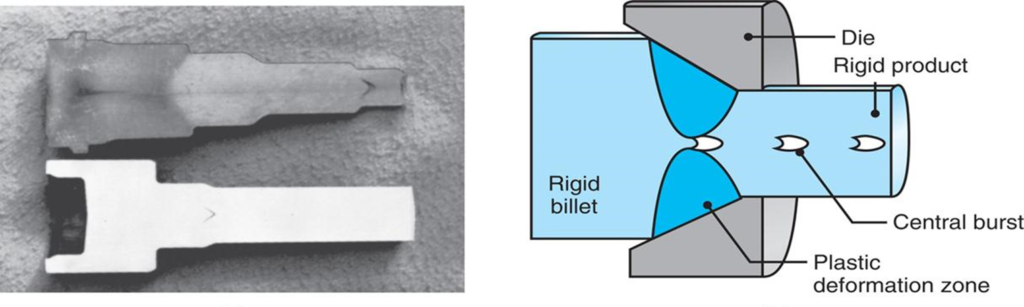
What are the three principal extrusion defects?
The three principal extrusion defects are surface cracking, Chevron cracking (central burst), and buckling. These defects can be caused by a variety of factors, including improper die design, temperature control, and material properties. Internal defects such as central bursts are dangerous because unless the products are inspected, such internal defects may remain undetected and later cause failure of the service part. The tendency toward chevron cracking increases if the two plastic zones do not meet. To reduce the likelihood of internal cracking the plastic deformation zone must be made larger by either decreasing the die angle or by increasing the reduction in cross-section. Other defects include:
- Aesthetic flaws (e.g., pits, black specs, pinholes, drag marks, die lines, sink marks)
- Size variance (which can be intermittent or contiguous)
- Dimensional variations.
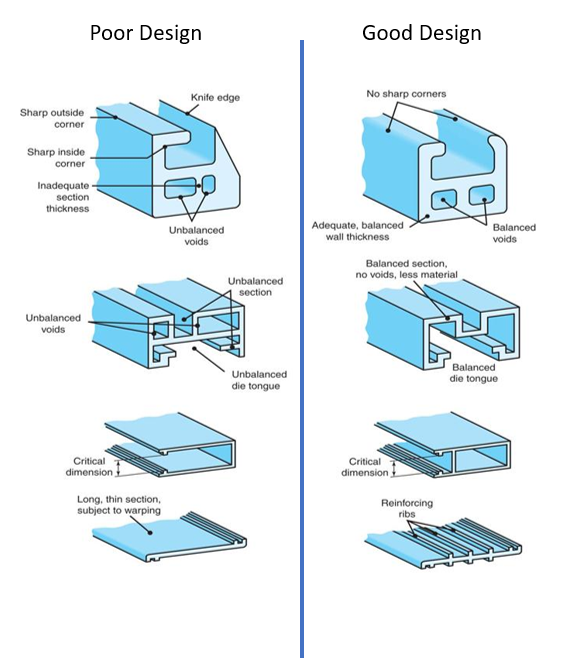
What are some good design practices for extrusion and drawing parts?
Good design practices for extrusion and drawing parts include considerations like:
- selecting the appropriate material
- designing to eliminate sharp corners keeping section thicknesses uniform
- and avoiding undercuts.
Conclusion
There you have it, folks! A beginner’s guide to extrusion manufacturing. We hope this article has given you a better understanding of what extrusion is, how it works, and some of the key factors that can impact the process and the final product. In addition to extrusion, most parts also may be made by casting, forging, or machining. Deciding what metalworking process is best for your specific application depends on the material’s part dimensions, wall thickness, and the properties desired. Economic considerations also are important in the final metalworking process selection. I hope you found this article informative and helpful. Thanks for reading!



Itís hard to come by knowledgeable people about this subject, but you sound like you know what youíre talking about! Thanks