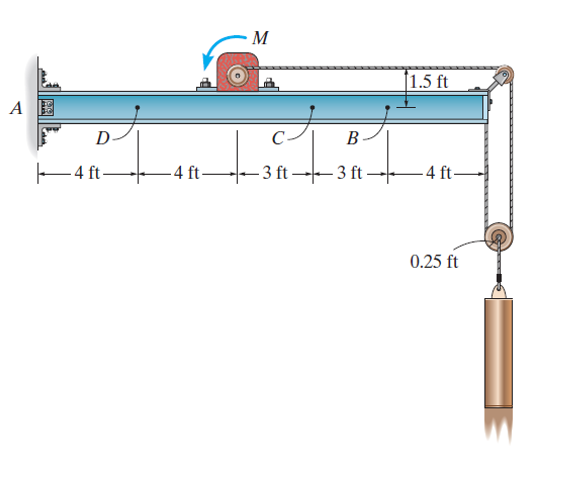
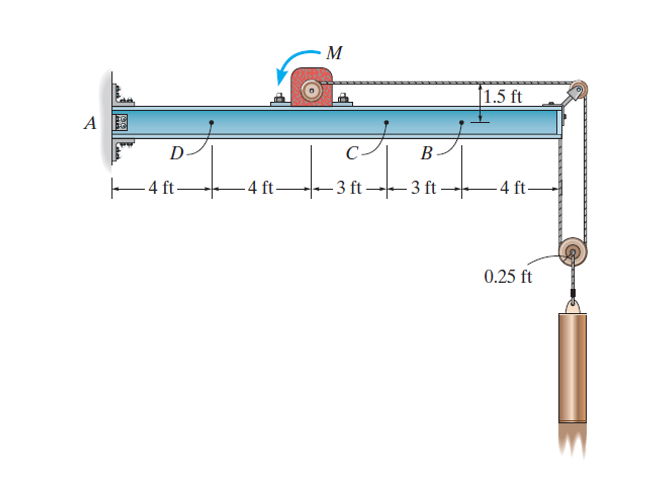
The Science of Fatigue Stress in Engineering: Key Considerations for Design and Testing
What is fatigue stress in engineering? So, what exactly is fatigue stress? Basically, it’s when a component or structure starts to weaken and break down over time due to cyclical stress or loading. Even if the stresses put on the component are within acceptable limits, fatigue failure can still occur due to the frequency of…