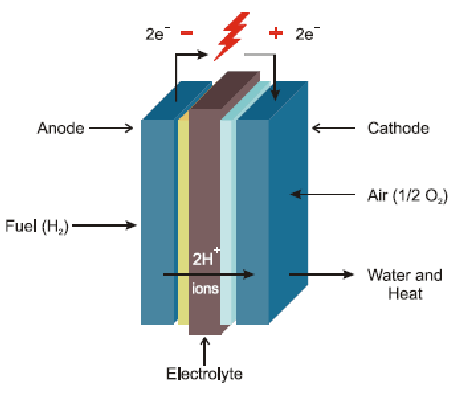
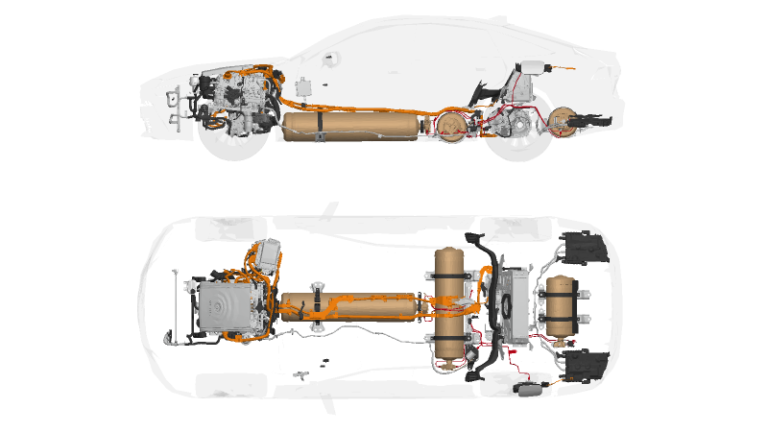
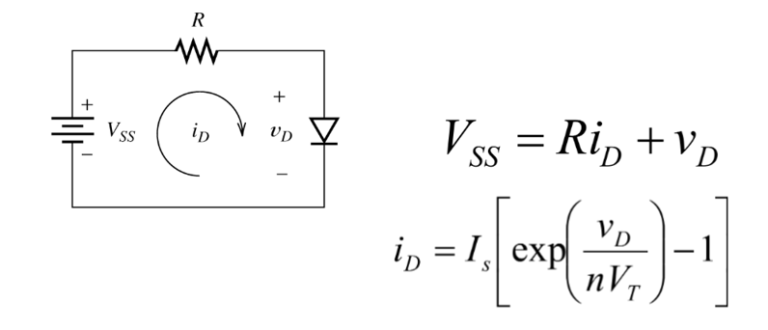Second Life Batteries
Abstract The Li-ion Second Life Batteries application is of growing interest with significant potential to address sustainability and environmental challenges. By 2040, an estimated 3.4 million kilograms of LIB cells from electric vehicles (EVs) could potentially enter the waste stream. However, these batteries still have many useful years ahead of them. Instead of being trashed,…