Why is Heat Transfer Important?
Heat transfer is a branch of thermal engineering that deals with the production, utilization, transformation, and interchange of thermal energy caused by variations in temperature, leading to changes in temperature distribution. The field of transport phenomena explores the transfer of momentum, energy, and mass through conduction, convection, and radiation.
Heat Transfer Background
In the early 19th century, scientists believed in the concept of caloric, an invisible fluid within bodies that was thought to transfer from hot to cold objects. Caloric was attributed with certain properties, some of which were found to be inconsistent with natural laws, such as having weight and being indestructible. For instance, when rubbing our hands together, both hands warm up even though they were initially at a lower temperature. If heat was due to a fluid, it would have moved from a hotter body with more energy to a colder one with less energy.
Thompson and Joule demonstrated the fallacy of the caloric theory. Heat is not a substance as originally believed, but rather a form of kinetic energy at the molecular level, according to the kinetic theory. The warmth generated by rubbing hands together is the result of kinetic energy from the motion (rubbing) converting to heat due to friction.
A system completely free from heat flow would need to be isothermal, with energy evenly distributed and perfectly insulated from its surroundings. Such conditions are impossible to achieve in reality.
What is the basic law of heat transfer?
As per the second law of thermodynamics, heat naturally moves from areas of higher temperature to those of lower temperature. Therefore, heat flow is considered positive when the temperature gradient is negative. The fundamental equation for steady-state, one-dimensional conduction is expressed as: qk = -kA (dT/dx), where qk represents heat flow, k is the thermal conductivity, A is the cross-sectional area, and (dT/dx) is the temperature gradient.
What is heat transfer and give an example?
Heat transfer is the exchange of thermal energy between physical systems. Heat energy is passed from one molecule to another as a result of their movement. There are three primary modes of heat transfer, conduction, convection, and radiation. Due to its effect on material selection, machinery performance, and reaction speed, heat transmission is essential in various different fields across different engineering disciplines, such as civil, mechanical, and chemical engineers.

What are the 3 types of heat transfer and how do they work?
There are three primary modes of heat transfer, are conduction, convection, and radiation.
- Conduction occurs when two objects are physically touching each other
- Convection occurs when a liquid or gas goes around an object.
- Radiation takes place between two objects that are not in direct physical contact with each other.

What is meant by heat conduction?
Thermal Conduction is the process by which heat is transferred between objects that are touching. Heat naturally wants to flow from hotter to colder until equilibrium is reached. The Internal temperature changes are due to the motion of electrons and atoms/molecules coming into contact with one another. The rate of heat transfer is influenced by the thermal conductivity of the material. The higher the conductivity, the faster the transfer of energy.

A good example of conduction is a hot frying pan on a stove. When the pan is heated, the heat is transferred from the stove burner through the metal of the pan and to the food being cooked. Other examples of conduction include the warming of your hands when holding a hot cup of coffee or the cooling of your feet when walking on a cold floor.
What is heat convection in simple words?
Convection is the transfer of thermal energy by the physical movement of fluids, such as liquids or gases from one location to another. The transfer of energy occurs as a result of the fluid moving from hotter to cooler regions, and it is influenced by the density of the fluid.
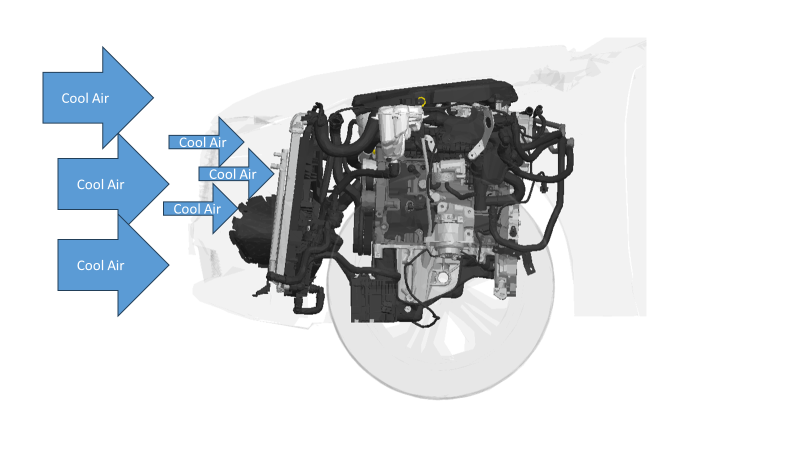
Heat convection is often the primary mode of energy transfer in liquids and gases. When a fluid is heated, it expands, becomes less dense, and rises, while cooler, denser fluid sinks to replace it. A classic example of convection is boiling water on a stove. As the water heats up, the warmer, less dense water rises to the surface, while the cooler, denser water sinks to the bottom. Another example of convection is cool air going though a radiator to help cool off the engine coolant.
What is the meaning of heat radiation?
All bodies constantly emit energy by a process of electromagnetic radiation. The intensity of this radiant. Energy flux depends on the temperature of the body and the nature of its surface. Radiation is the transfer of heat when bodies are not in direct physical contact with each other or when they are separated by a space. Radiation heat transfer happens through electromagnetic waves, such as visible light or infrared radiation. Unlike conduction and convection, radiation does not require a medium to travel through, and it can occur in a vacuum.
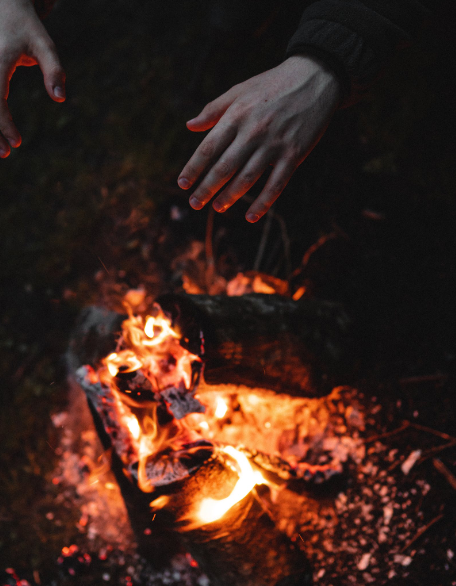

The rate of radiation is influenced by the temperature of the emitting body, with hotter objects emitting more radiation. Very often, the emission of energy, or radiant heat transfer, by cooler bodies can be neglected in comparison with convection and conduction. Most of the heat that reaches you when you sit in front of a fire is radiant energy. Radiant energy browns your toast in an electric toaster, and it warms you when you walk in the sun.
What is a Heat Exhangers
Heat exchangers are employed to enhance heat transfer efficiency or to disperse heat. They find extensive application in refrigeration, air conditioning, space heating, power generation, and chemical processing. In simple terms, a heat exchanger is a device that moves heat from one substance to another.
Heat Exhanger Examples
A typical example of a heat exchanger is a car’s radiator, where the hot coolant is cooled by air passing over the radiator’s surface. Hydraulic Oil Cooler removes heat from hot oil using cold water or air. Similarly, a Swimming Pool Heat Exchanger heats pool water using hot water from a boiler or a solar-heated water circuit.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heat transfer plays a crucial role in numerous aspects of our lives. From the comfort of our homes and offices to the efficiency of industrial processes. Understanding heat transfer mechanisms helps us design more efficient systems, conserve energy, and innovate new technologies. Whether it’s in the cooling of electronics, the heating of buildings, or the generation of electricity, the principles of heat transfer are fundamental to our modern way of life. By appreciating its significance, we can continue to develop sustainable solutions and improve our quality of life.