Understanding Solar Energy
Solar energy refers to any form of energy produced by the sun. It is generated through the process of nuclear fusion that occurs within the sun. Solar radiation, also called electromagnetic radiation, is the light emitted by the sun due to nuclear fusion. Although every location on Earth receives sunlight throughout the year. The intensity of solar radiation reaching a specific spot on the Earth’s surface varies. Solar technologies harness this radiation and convert it into usable forms of energy.
Solar power, also referred to as solar electricity, is the process of converting sunlight into electricity. This is done either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly through concentrated solar power. Photovoltaic panels harness the photovoltaic effect to transform light into an electric current. On the other hand, concentrated solar power systems utilize lenses, mirrors, and solar tracking systems to concentrate a large area of sunlight onto a hot spot. This energy can be used to generate electricity (typically using a steam turbine) or be stored in batteries or thermal storage.
Utilization of solar energy
There are two main types of solar energy technologies photovoltaics (PV) and concentrating solar-thermal power (CSP). Photovoltaics are typically primarily used for small and medium-sized applications. PV systems can be found from calculators powered by a single cell to remote homes powered by off-grid rooftop systems. The first commercial concentrated solar power plants were developed in the 1980s.
As the cost of solar panels has decreased, the capacity and production of grid-connected solar PV systems have roughly doubled every three years. Currently, three-quarters of new generation capacity comes from solar. With millions of rooftop installations and gigawatt-scale photovoltaic power stations still being constructed.

In 2023, solar power generated 5% of the world’s electricity, compared to 1% in 2015 when the Paris Agreement to limit climate change was signed. Alongside onshore wind, utility-scale solar offers the cheapest levelized cost of electricity for new installations in most countries. Nearly half of the solar power installed in 2022 was rooftop.

To meet the demands of electrification and combat climate change, a significant increase in low-carbon power generation is necessary. The International Energy Agency highlighted in 2022 that greater efforts are required for grid integration and to address policy, regulation, and financing challenges.
Why is solar the best energy source?
Using solar panels to generate electricity produces no greenhouse gas emissions, making it a clean energy source. Solar power is considered essential for clean energy production due to the abundance of energy provided by the sun.
How does solar energy work without electricity?
During a power outage, solar panels cannot supply electricity to your home or business. However, two exceptions exist: if your system includes energy storage, or if you choose an off-grid system over the benefits of grid-tied solar.
Why is Solar Energy Important?
First of all, the Earth receives an immense amount of solar radiation, about 174 petawatts (PW), in the upper atmosphere. Approximately 30% of this solar radiation is reflected in space. The other 70% is absorbed by clouds, oceans, and land masses. This absorption of solar radiation is what raises the temperature of Earth’s land surface, oceans, and atmosphere. It plays a significant role in maintaining the planet’s temperature balance, keeping the surface at an average temperature of 14 °C, which is crucial for sustaining life as we know it.

Additionally, solar radiation is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants use to convert solar energy into chemical energy. This process is fundamental as it produces food, wood, and biomass, which are crucial for life on Earth. Furthermore, fossil fuels, which are derived from biomass, are also a product of this process and are a major source of energy for modern society.

How does photosynthesis turn solar energy into usable energy?
Photosynthesis transforms electromagnetic radiation into chemical energy. By producing various products such as building blocks, biofuels, and biomass. Photosynthesis captures approximately 3,000 EJ per year in biomass. This process is crucial for life on Earth as it forms the basis of the food chain and provides the raw materials for fossil fuels.
Yearly Solar fluxes & Human Energy Consumption
Solar radiation is an incredibly abundant and renewable resource that has the potential to revolutionize the way we produce and consume energy. Each year, the Earth absorbs an astounding 3,850,000 exajoules (EJ) of electromagnetic radiation through its atmosphere, oceans, and land masses. To put this into perspective, the total energy used by mankind in 2005 was only 487 EJ, making solar energy a vastly underutilized resource.

In terms of electricity generation, solar power accounted for 56.7 EJ in 2005, representing a mere 0.0015% of the total electromagnetic radiation absorbed by Earth. This figure underscores the immense potential for growth in the solar energy sector. It has been noted that in 2002, the amount of solar energy reaching the Earth’s surface in just one hour was more than the world used in the entire year. This highlights the vastness of solar energy as a power source.
The sheer magnitude of electromagnetic radiation reaching the Earth’s surface is staggering. In one year alone, the amount of solar energy is approximately twice as much as could ever be obtained from all of the Earth’s non-renewable resources of coal, oil, natural gas, and mined uranium combined.
What are some advantages of solar energy?
Solar energy offers several advantages that make it an attractive alternative to traditional energy sources. First of all, it is clean and non-polluting, producing no harmful emissions that contribute to air pollution or climate change. Additionally, solar radiation is renewable, meaning it is continuously replenished by the sun, making it a sustainable energy source for the long term.

Solar cells, which are used to convert solar energy into electricity, operate silently and do not produce any noise pollution. They also require very little maintenance, reducing the overall operational costs. Moreover, solar energy systems are long-lasting, with a lifespan of up to 25 years or more, and can be installed almost anywhere, making them suitable for both urban and remote locations.
One of the most significant advantages of solar energy is that it eliminates fuel costs and the associated supply problems. Since solar radiation is derived from sunlight, which is freely available, there are no ongoing fuel expenses once the solar energy system is installed. Overall, these advantages make solar energy a reliable, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly energy solution for the future.
What are some disadvantages of solar energy?
Despite its immense potential, solar energy does pose challenges, particularly as an intermittent resource. Solar and wind energy, both reliant on weather conditions, raise issues related to grid stability and energy storage. However, advancements in technology, such as improved energy storage solutions and grid management systems, are helping to mitigate these challenges.
Another major drawback is the high initial cost of installing solar panels. Although prices have been decreasing over the years, the upfront investment can still be significant for many homeowners and businesses. Finally, another limitation is that solar energy may not be suitable for every roof type. Factors such as shading, roof orientation, and available space can impact the efficiency of solar panels. Thus making solar cells less effective or impractical for some buildings. Despite these challenges, ongoing advancements in technology and decreasing costs are helping to make solar energy a more viable option.
What are some applications of Solar energy?
Solar energy finds a wide range of applications across various sectors. In domestic settings, solar energy is commonly used to power appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, televisions, lighting systems or even your home.

Solar energy is also extensively utilized in ocean navigation aids, with many lighthouses and buoys powered by solar cells. This is particularly useful in remote or offshore locations where access to traditional power sources may be limited.
Telecommunication systems also benefit from solar energy, with radio transceivers on mountaintops and telephone boxes in rural areas often being powered by solar panels. This allows for reliable communication infrastructure in areas where grid power may be unreliable or unavailable.
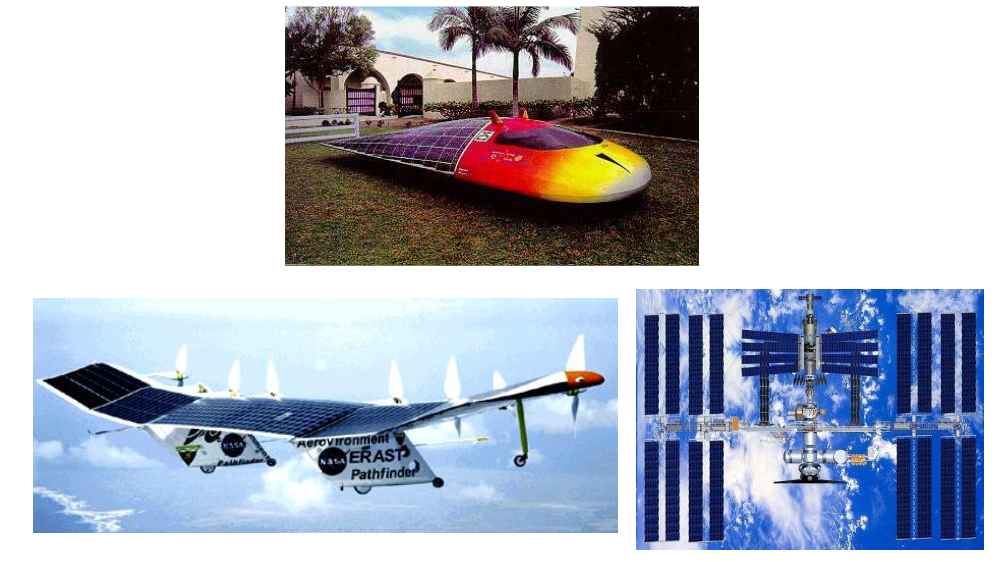

In addition, solar energy plays a crucial role in electric power generation in space. Solar panels are used to provide electrical power to satellites orbiting the Earth, allowing them to function effectively without the need for frequent maintenance or refueling. This application demonstrates the reliability and versatility of solar energy as a power source even in the most challenging environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, solar energy offers a vast and sustainable solution to our energy needs. By harnessing the power of the sun, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and decrease harmful emissions that contribute to climate change. Understanding the basics of solar energy, from the photovoltaic effect to the construction of solar cells, is crucial in realizing the full potential of this renewable resource. As technology continues to advance, the cost of solar energy continues to decrease, making it an increasingly viable option for both individuals and communities around the world. Embracing solar energy not only benefits the environment but also helps to create a cleaner, brighter future for generations to come.