Circuitry 101: Exploring Basic Electrical Circuit Principles
Introduction
Today, we’re diving into the exciting world of basic electrical circuits. You might be wondering, “Why should I bother learning about circuits?” Well, let me tell you, understanding electrical circuits is like unlocking a secret language that surrounds us in our daily lives. From the lights that brighten up our rooms to the gadgets we can’t live without, circuits are everywhere! So, grab a seat, and let’s demystify the fundamentals of electrical circuits in a fun and easy-to-understand way.
What is an Electrical Circuit?
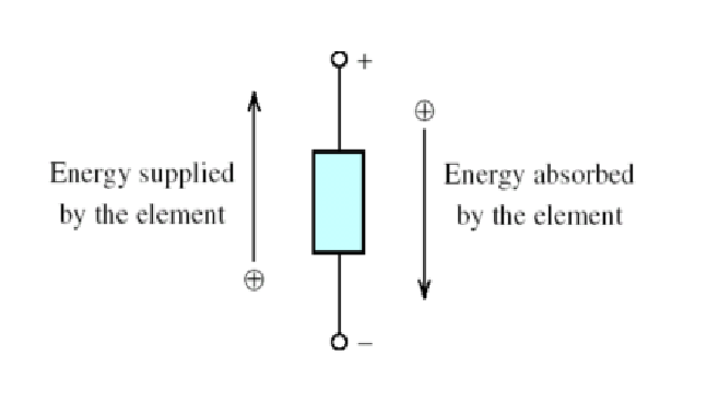
Alright, let’s start at the beginning. Imagine you’re driving on a road trip with your friends. You’re all sitting in a car, traveling from point A to point B. Now, think of an electrical circuit as the road you are traveling on. It’s a loop or pathway through which electric current flows. For electricity to flow the element/ circuit must have a voltage (or potential difference) difference from point A to point B. Energy is either consumed (absorbed) or supplied by the elements in the circuit when charge flows through the elements.
Typical Electric Circuit Components
In a basic electrical circuit, you’ll find a few key components:
- Power Source: The life force of the circuit, providing the energy needed for everything to work. Just like you need fuel to keep your car moving, the power source keeps the circuit energized and ready to go. Common power sources include batteries and voltage/ current source (an example is a electrical outlets in your home that supply electricity).
- Resistors: These components restrict the flow of electric current in a circuit. They’re like speed bumps that control the flow of traffic. Resistors are crucial for adjusting voltage levels, limiting current, and protecting sensitive components.
- Capacitors: Capacitors store electrical energy and release it when needed. They act like temporary storage tanks, storing and releasing charges. Capacitors are commonly used in filters, timing circuits, and power supply stabilization.
- Inductors: Inductors store energy in a magnetic field when current passes through them. They resist changes in current flow, acting as energy storage devices. Inductors are found in power supplies, motors, and audio equipment.
- Diodes: Diodes allow current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. They act like one-way valves, ensuring current flows properly. Diodes are commonly used in rectifiers, voltage regulators, and signal processing circuits.
- Transistors: Transistors are the building blocks of modern electronics. They amplify or switch electronic signals and can control the flow of current. Transistors are vital in amplifiers, computer processors, and communication devices.

These are just a few examples of typical electric circuit components. Each component plays a specific role in controlling and manipulating electrical signals, enabling the functionality of electronic devices that we use daily. Understanding these components is essential for circuit design, troubleshooting, and expanding your knowledge of electronics.
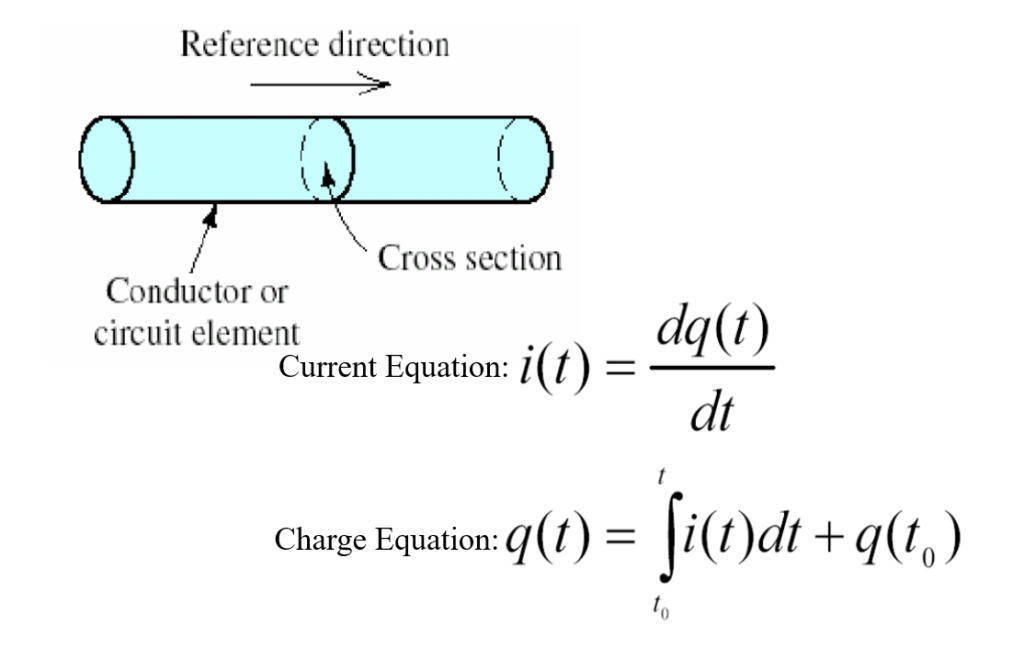
What is the electric current and charge?
Electric current is the time rate of flow of electric charge through a conductor or circuit element. It is the movement of electrons or other charged particles in a specific direction. Electric charge, on the other hand, is the fundamental property of matter that determines its electromagnetic interactions. It can be positive or negative, with like charges repelling each other and opposite charges attracting. Electric current is the result of the flow of electric charge in a circuit.
What is voltage in simple terms?
Now, let’s talk about voltage. Think of voltage as the driving force behind electric current. It’s like the pressure that pushes the current through the circuit (charged electrons). You can imagine it as the speedometer on your car, determining how fast you’re going. Voltage is measured in volts (V), and different devices and circuits require specific voltages to function properly.
Is electrical power and energy the same?
Electrical power and energy are not the same, although they are related. Electrical power refers to the rate at which electricity is consumed or produced. It is measured in watts (W) and represents the amount of energy transferred per time rate. Electrical energy, on the other hand, is the total amount of work done or energy consumed over a period of time. It is measured in watt-hours (Wh) or kilowatt-hours (kWh) and represents the cumulative amount of energy used or produced.
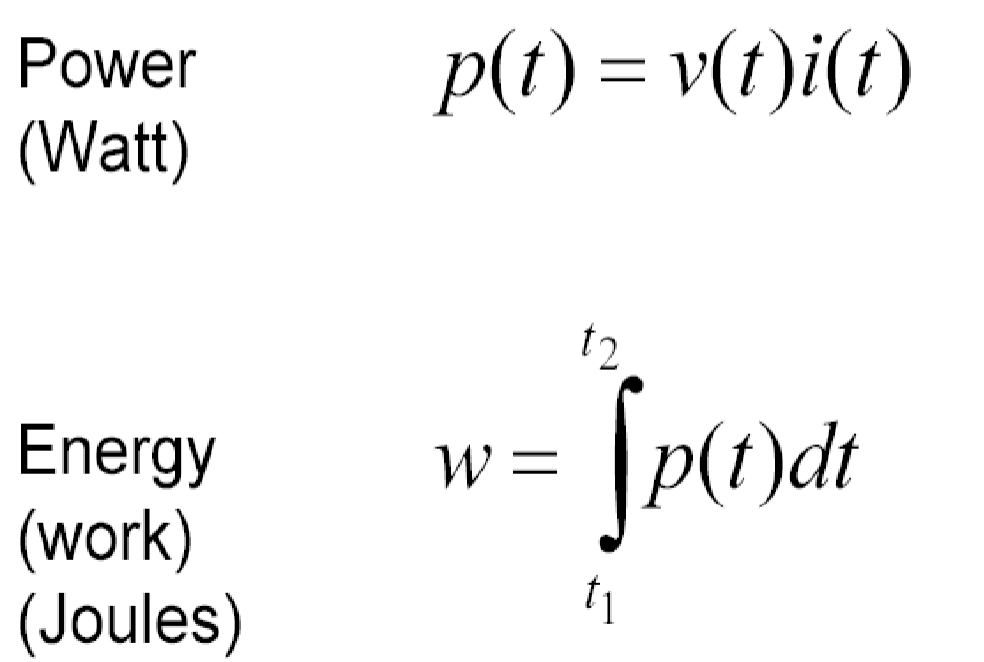
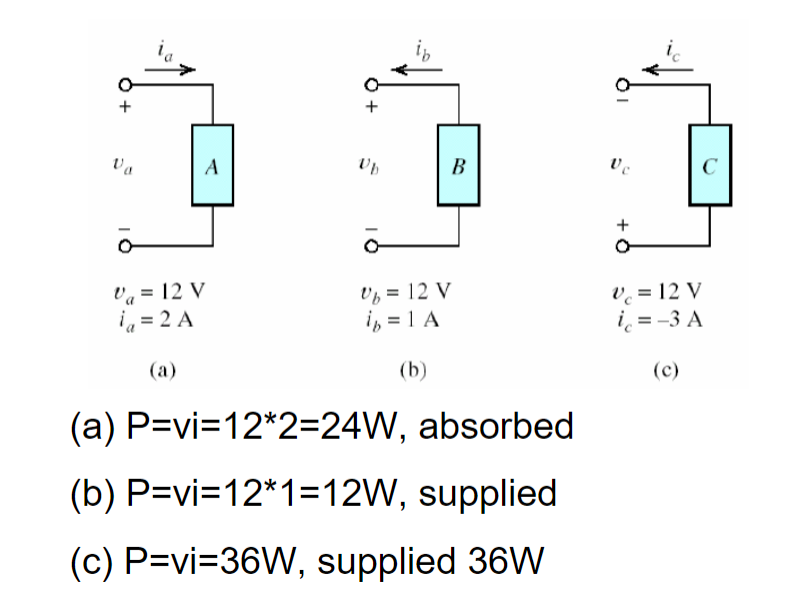
Sample Problem:
Determine the power for each of the following circuits and indicate if its absorbed or supplied:
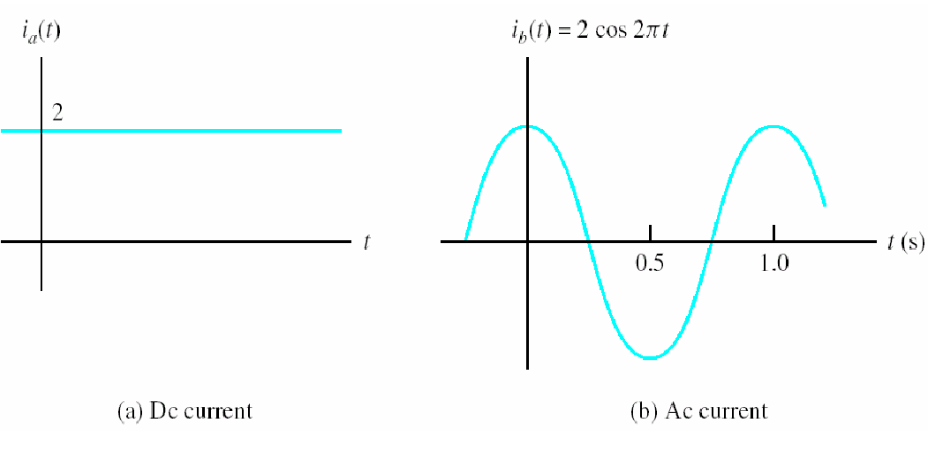
What is the difference between AC and DC current?
It’s important to mention that there are two types of current: direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC). In direct current, the voltage is always constant, and the electricity flows in one direction, just like water flowing through a pipe. Batteries, for example, provide DC power. On the other hand, AC changes direction periodically, like the waves crashing on the shore. AC power is what we typically get from the electrical outlets in our homes.
Load: Putting Electricity to Work
Now that we’ve covered power sources and conductors, let’s talk about the load. The load is where the magic happens—it’s the part of the circuit that actually consumes electrical energy and puts it to work. Think of it as the destination of your road trip, where you and your friends have a blast.
Loads come in various forms. For example, a light bulb is an examples of common electrical loads. When you turn on the switch, the current flows through the circuit and reaches the light bulb, causing it to illuminate the room. The light bulb is converting electrical energy into light energy, creating a cozy ambiance.

But loads aren’t limited to just light bulbs. DC Motors, like the ones that you find in battery powered RC toy car, are another type of load. When you switch them on, they convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, making the motor thus turing the wheels of the car.

Another important concept to mention here is resistance. Resistance is like the obstacle course that your car encounters on the road trip. It’s the property that determines how much a material or component resists the flow of electric current. Some loads, like light bulbs, have a higher resistance, while others, like conductors, have low resistance. The unit of measurement for resistance is the ohm (Ω).
Switch: Controlling The Circuit
Last but not least, let’s talk about the switch. The switch is like the traffic cop of the circuit. It allows us to control the flow of electricity, just as you control your car’s movements with the steering wheel and pedals.
A switch can turn a circuit on or off. It’s like the power button on your favorite device. When you flip the switch, you’re allowing the current to flow through the circuit and power up the load. Imagine having the ability to turn the lights on or off with just a flick of a switch—it’s all thanks to this simple yet essential component.

Switches come in various types and designs. You might be familiar with toggle switches, like the ones you find on your room’s light switch. With a flick up or down, you can control whether the lights are on or off. Push buttons are another common type of switch, like the ones you find on your TV remote or your gaming console controller. You press the button to activate or deactivate a function.
Switches are not only convenient but also crucial for safety. They allow us to easily disconnect the circuit when needed, preventing accidents or damage to the devices connected to the circuit. Think of it as having a quick emergency brake for your car—it gives you control and keeps everyone safe.
Conclusion
And there you have it—Circuitry 101: Exploring Basic Electrical Circuit Principles. We’ve taken a road trip through the world of circuits, understanding their key components and how they work together. We’ve learned about power sources, conductors, loads, and switches—the building blocks that make up the circuits powering our everyday lives.
Remember, understanding basic electrical circuits is not only fascinating but also empowering. It allows you to have a deeper appreciation for the technology around you and opens doors to exploring more complex concepts in the future. So, next time you turn on a light, charge your phone, or use any electronic device, you’ll have a better understanding of the circuitry behind it.