Understanding Car Design
Automotive design is a creative process that defines the physical appearance of vehicles, including cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Automotive designers are responsible for styling a vehicle’s interior and exterior. You might love or hate the design of a car, but there is no doubt that car design plays a big role in the development of a vehicle. One of the reasons the automobile industry has the following worldwide is because the vehicle development process requires automotive engineers and creative designers to come together. They create a product that is aesthetically appealing and on the cutting edge of technology.
What is the Function of a Car Designer?
Have you ever seen a drawing of a concept car and been blown away by how amazing it looks? Have you then wondered why no manufacturer has made it? If this car is so perfect in every way, it’s probably because the car defies the laws of physics. Or it would be so expensive nobody would buy it. Or the final production vehicle wouldn’t look anything like the original concept. As a result, the primary function of automotive designers is to design an aesthetically pleasing vehicle. This vehicle should differentiate itself in an already crowded market while balancing aerodynamics, manufacturing, engineering, and safety criteria.

This process is a delicate balance where engineers and designers need to give and take to achieve the intended mission of the vehicle. For example, the exterior designer might incorporate specific shapes such as curves and rounded-off edges to achieve aerodynamic efficiency even though they might prefer shoulders and wedges to have a more aggressive-looking vehicle.

Interior designers face the same challenges but are more focused on arranging the car’s components while maintaining aesthetics and comfort. They also choose materials for various parts of the vehicle, including fabric, plastic, and metal. They also select trim packages, which include paint patterns, bumpers, and wood trims.
History of Car Design
In the 1920s, automotive design in the United States underwent a significant change as the national automobile market became saturated. To maintain sales, General Motors’ head, Alfred P. Sloan Jr., proposed annual model-year design changes to persuade car owners to buy new replacements each year. This idea, inspired by the bicycle industry, was later termed “planned obsolescence,” although Sloan preferred the term “dynamic obsolescence.”
The Merging of Creative Car Design and Engineering
Before Harley Earl (November 22, 1893 – April 10, 1969) cars were engineered period. It wasn’t until Lawrence P. Fisher, general manager of the Cadillac division of GM was on a business trip to California that the idea of styling mass-market vehicles came to be. L. Fisher was inspired by Earl’s designs and techniques, particularly his use of modeling clay to shape his designs. Fisher convinced Earl to join him in Detroit and eventually Art and Color Section of General Motors was born. This group would eventually turn into GM’s Design Studio.

What car company started using clay models and in what year?
Clay modeling’s roots can be traced back to the 1930s at General Motors. Harley Earl, the leader of GM’s styling studio, pioneered transforming sketches into full-scale models using pliable clay. The success of Earl’s department leads to all other car companies copying the concept of hiring creative design studio staff to also make their vehicles aesthetically prominent. If you are interested in learning more I recommend reading Fins: Harley Earl, the Rise of General Motors, and the Glory Days of Detroit.
Is it hard to be a car designer?
If it wasn’t clear already automotive creative designers and engineers are not the same thing. Car designers go to art school while automotive engineers get an engineering degree. However, due to the appeal of getting paid full-time to draw and sketch cars this job is highly competitive. There are specialized schools such as the College of Creative Studies in Detroit MI which have majors in Transporation Design. Many of the automotive creative staff have graduated from this university since they have direct ties to the neighboring automotive giants. To be considered for a car design position most companies will require a bachelor’s degree, as well as an outstanding portfolio to demonstrate your artistic skills and relevant field experience/internships.
How are cars designed?
Automotive designers begin by translating their ideas into hand-drawn sketches, which are then developed into CAD (computer-aided design) models using 3D software. However, these early steps are not enough to fully evaluate the design.

The next steps involve bringing their ideas into the physical world. Designers create reduced/full-scale models using industrial plasticine clay, which is used for aerodynamics testing and to evaluate the size and proportions of the initial design.
Design Studio Output to Automotive Engineers
Throughout the vehicle development process, the design studio provides the engineering staff with periodically updated styling surfaces. These styling surfaces are to ensure that the design studio’s vision is not too far from engineering’s capability. The automotive engineering teams, then take this tangible representation of the envisioned vehicle and evaluate it to its engineering criteria.
The styling surface provided to engineering staff can be in many different forms. Some examples are sketches, which are initial conceptual drawings that capture the essence of the design. Renderings, on the other hand, are digital or hand-drawn images that are further refined for design details and aesthetics. Full-size drawings (also known as general assembly drawings) offer a detailed blueprint of the vehicle’s exterior and interior features/ as well as occupant packaging. Foam core mock-ups and models provide a three-dimensional representation of the design, allowing for a physical assessment of the proportions and shape of the vehicle.
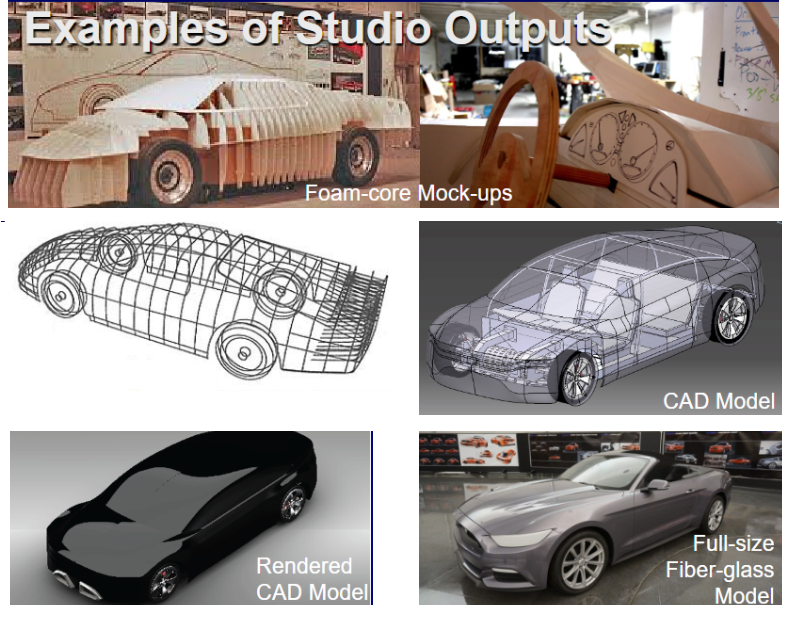
Clay models, a longstanding tradition in automotive design, offer a tactile and realistic representation of the vehicle’s design, allowing for further refinement. Milled and clayed models are more advanced versions, typically used for aerodynamic testing and fine-tuning of design details. Fiberglass models, both exterior and interior bucks, offer a more durable and detailed representation of the final design. Finally, the full vehicle model integrates all these elements into a comprehensive representation, providing a holistic view of the design for the engineering teams to evaluate and refine further.
Car Design: Key Design Considerations
When designing a car, several key considerations must be taken into account. First of all, the vehicle’s class, type, size, and weight are crucial factors that determine its intended use and target market. Understanding customer preferences and satisfaction targets is also essential, as it influences design choices regarding features, aesthetics, and performance.
A key principle in car design is to prioritize the comfort, convenience, safety, and security of the occupants. This involves designing the interior layout and features to maximize usable space while minimizing the space taken up by hardware. Additionally, performance and hardware functionality must be carefully balanced to meet the desired performance metrics without compromising other aspects of the vehicle’s design.
Another important consideration is to design the vehicle as a system, taking into account all attributes simultaneously. This holistic approach ensures that the various components and features of the vehicle work together seamlessly to deliver the desired performance and user experience. Finally, the perception of quality is crucial, as it influences customers’ perceptions of the brand and their overall satisfaction with the vehicle.
Car Design Process
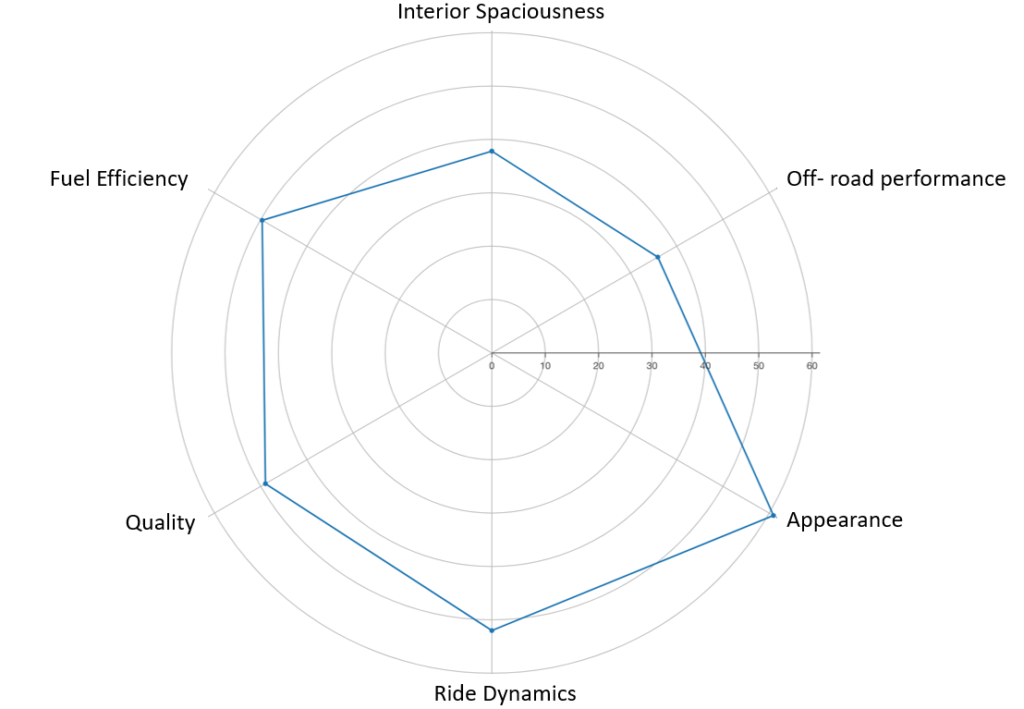
The advanced design process in automotive design typically starts with establishing the vehicle program assumptions and progresses through various stages to parameter/target selection. Initially, the process involves defining the assumptions and goals of the vehicle program, such as the market segment, target customers, and performance targets. This is usually captured in a vehicle radar/spider chart.
Market research is then conducted to understand customer preferences, trends, and competitive offerings, leading to the development of initial design concepts. These concepts are refined based on feedback from various engineering teams, feasibility studies, and design reviews, often involving the creation of sketches, renderings, and digital models for evaluation by various parts of the organization.

Design validation follows, where the selected concept is tested through computer simulations CAE/ CFD models, scale models, and prototype testing. This is done to ensure the vehicle meets performance, safety, and regulatory requirements. Parameters and targets are then set for various aspects of the vehicle, guiding the detailed design phase. This phase includes exterior and interior styling, engineering specifications, and materials selection, often using CAD tools.
Prototypes are built for testing and validation in wind tunnels, on test tracks, and in simulated real-world conditions, usually at a company’s proving grounds. Once the design is finalized and validated, it is prepared for production. This includes finalizing engineering drawings, selecting suppliers, and setting up production processes. The vehicle is then launched in the market, with marketing efforts to promote it and gather feedback for future improvements. Throughout this process, close collaboration between designers, engineers, marketers, and other stakeholders ensures that the final product meets customer needs while meeting technical and regulatory requirements.
Do car manufacturers still make clay models?
Car designers employ clay models to visualize their concepts and verify that their designs are visually appealing and practical. This method has been integral to the car design process for many years and remains a standard practice in the industry.

Who can design a car?
A car is by many individuals, the artistic designers are responsible for the aesthetics of the vehicle, while engineers are responsible for the design of specific components or systems to bring the aesthetic vision of the vehicle to life. As a result, a degree in automotive design from an art school or automotive engineering is preferable.
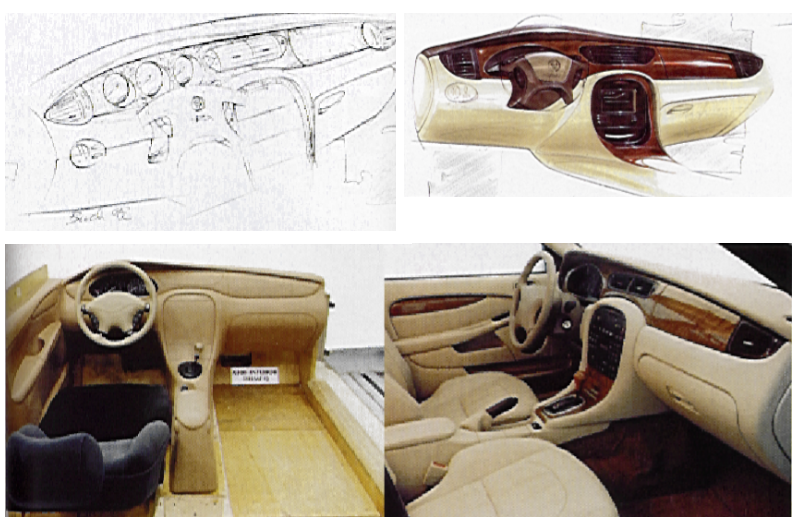
Interior Design
The interior designer of vehicles focuses on the proportions, shape, placement, and surfaces of components like the instrument panel, seats, door trim panels, headliner, and pillar trims. The priority lies in ensuring ergonomic design and passenger comfort. The design process mirrors exterior design, starting with sketches, and then digital and clay models.
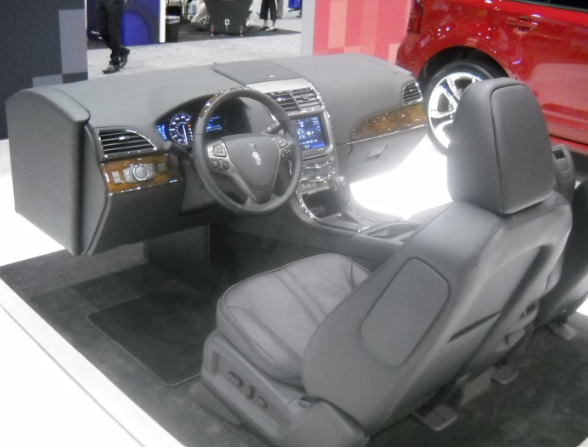

What is a seating buck?
The Seating buck is a physical model of a passenger car cabin used to verify ergonomics. It is commonly employed to evaluate comfort, ease of entry and exit, visibility, and overall livability.

Exterior Design
The design team responsible for the vehicle’s exterior works on the proportions, shape, and surface details. They start with manual sketches and digital drawings, gradually developing more detailed drawings. These drawings are then digitally rendered. Consumer feedback is crucial at this stage to refine vehicle concepts for the target market.

After further refinement, industrial cars or digital models are created based on the drawings and images. These models are used to produce quarter-scale and full-sized mock-ups of the final design. Clay models are still essential for evaluating the exterior design, despite advancements in photorealistic software and virtual models nothing beats looking at a real representation of a vehicle in natural light.
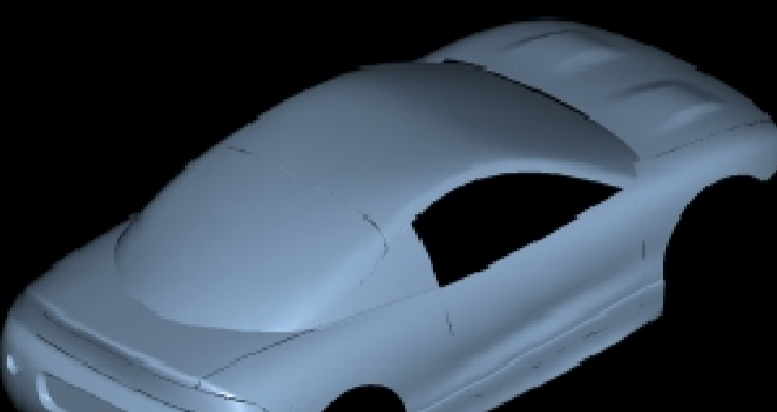

What are the advantages and disadvantages for an automotive designer to create a scale model?
Creating a scale model in automotive design has its advantages and disadvantages. One advantage is that scale models can save development time by providing a tangible representation of the design without the need to create a full-sized prototype. This can help designers quickly iterate and refine their ideas.

However, a disadvantage of scale models is that it can be difficult to accurately estimate size and space compared to a full-sized model. This can potentially lead to issues with the final design, especially in terms of ergonomics and functionality.
Automotive Design or Engineering?
It’s okay not to know which you prefer at this point, but remember, almost any intelligent, disciplined person can become an engineer. It helps if you excel at math, enjoy problem-solving, and are comfortable with computers. Most individuals with a passion for engineering and the mentioned skill set can secure a professional engineering position in some capacity upon graduation.
To become a professional car designer, you must be fully committed. Why? Because there are limited job openings each year and far more graduates than positions available. You must stand out and bring a fresh perspective to the field. You must have a strong voice and a desire to make a significant impact. This level of commitment demands thousands of hours of practice and a willingness to embrace new ways of thinking.
Why pursue this path despite the challenges? Nothing compares to the feeling of seeing an idea you once envisioned become a reality on the road or at an auto show. Getting a chance to see a vehicle that you helped design/ engineer will bring you immense joy. It’s a fulfillment that no one can take away.
Conclusion
In conclusion, car design is a multifaceted and dynamic field that combines creativity, engineering, and consumer psychology. Car Designers are responsible for creating vehicles that are not only functional but also visually appealing and emotionally engaging. From the initial concept sketches to the final production models, every step of the design process plays a crucial role in shaping the identity and success of a vehicle. By understanding the key principles and considerations that drive car design, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the artistry and innovation behind the cars we drive every day.