Automotive Transmission
A transmission, also known as a gearbox, is a mechanical device that utilizes a set of gears working in tandem. In a car, the transmission, or gearbox, serves as the mechanism that transfers power from the engine to the wheels. It does this through a system of gears and gear trains. It enables the driver to apply power to the vehicle in a controlled way, which is essential for efficient movement. Without a transmission, the car wouldn’t be able to move effectively.
History of the Automotive Transmission
The first commercially produced automotive transmissions were basic manual gearboxes. In the early days cars were not affordable for everyone. As a result, the roads were not designed for the high speeds so cars were not built for such speeds. Most early cars with a standard gearbox had one reverse gear and two forward gears.
Similar to modern manual gearboxes, drivers used a clutch pedal and a shift lever to select gears. The clutch pedal disengaged the motor input from the transmission, preventing the gears from forcibly turning as they meshed together. The shift lever aligned the appropriate gear with the motor input.
In the past two decades, there have been significant advancements in the design and application of automatic transmissions and drivelines. These include new innovations such as hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) transmissions, dual-clutch transmissions (DCT), continuously variable transmissions (CVT), torque vectoring differentials (TVD), and four-wheel drive (4WD) systems.
Do cars need transmission?
Most of today’s automobiles are powered by gasoline or diesel internal combustion engines. Which offer advantages such as better efficiency, higher energy storage capacity, and a favorable power-to-weight ratio. However, IC engines have certain drawbacks, including their inability to produce torque from zero speed. An IC engine delivers maximum power only at a specific engine speed. As a result, its fuel efficiency is directly influenced by its operating parameters. Therefore, a mechanism is needed to shift between different modes of operation, each providing various speed and torque ratios to suit the driver’s needs. This is precisely the role of the transmission.
A transmission system is crucial for the vehicle’s performance and fuel efficiency. It transmits power from the engine’s crankshaft to rotate the drive shaft. The transmission system consists of an interconnected assembly of gears and electrical components that facilitate power transfer from the drive shaft to the driven shaft, ensuring the vehicle maintains an optimal speed for maximum performance. The transmission can reduce higher engine speeds to lower wheel speeds, thereby increasing wheel torque.
The importance of a transmission system in the context of a vehicle’s fuel economy is undeniable. Transmission can impact fuel economy through power losses during transmission, such as churning of lubricant oil, drag caused by bearings, minor losses at the meshing of gears, and the inertia of rotating transmission components.
How do transmissions work?
Inside the transmission, a series of gears regulate the speed and torque of the wheels. The transmission achieves this through various gear ratios and the ability to shift between them as speed changes. Shifting can be done manually or automatically, and different transmission systems are tuned to provide various performance levels. Transmission systems are categorized into two types: manual and automatic.
Which is better, FWD or RWD?
Choosing between front-wheel drive (FWD) and rear-wheel drive (RWD) depends on your priorities. FWD vehicles, are lighter and typically offer more cabin space than RWD vehicles. They are preferred by drivers who want to minimize fuel consumption. On the other hand, RWD vehicles provide a more balanced driving experience. As a result, they are favored by performance enthusiasts and truck buyers who need maximum torque. Ultimately, your decision should be based on whether you prioritize fuel efficiency and cabin space (FWD) or performance and torque (RWD).
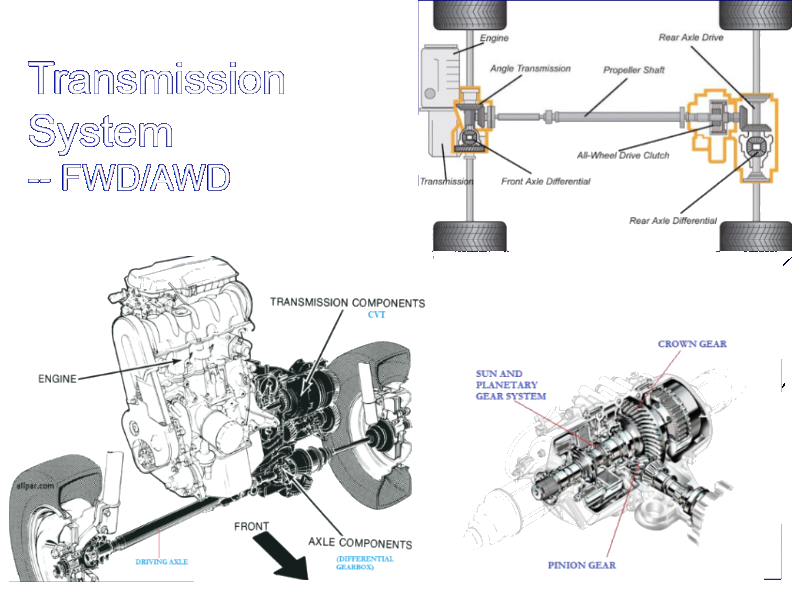
Manual Transmission
Manual transmission, also known as a manual gearbox, puts the driver in control. The manual gearbox allows the diver to change the gear ratios. This control is facilitated through the use of a shift lever, which the driver manipulates to engage different gears.
A manual transmission uses a clutch, typically engaged or disengaged by a foot-operated pedal, to transfer torque from the drive shaft to the transmission box and gear selector. In a vehicle, the flywheel is connected to the engine’s crankshaft. A clutch disk is between a pressure plate and the flywheel and pressed onto the flywheel by the pressure plate. If the vehicle moves and the clutch is engaged, the flywheel transfers rotation to the clutch plate and eventually to the wheels. When the clutch is pressed, however, a separation occurs.
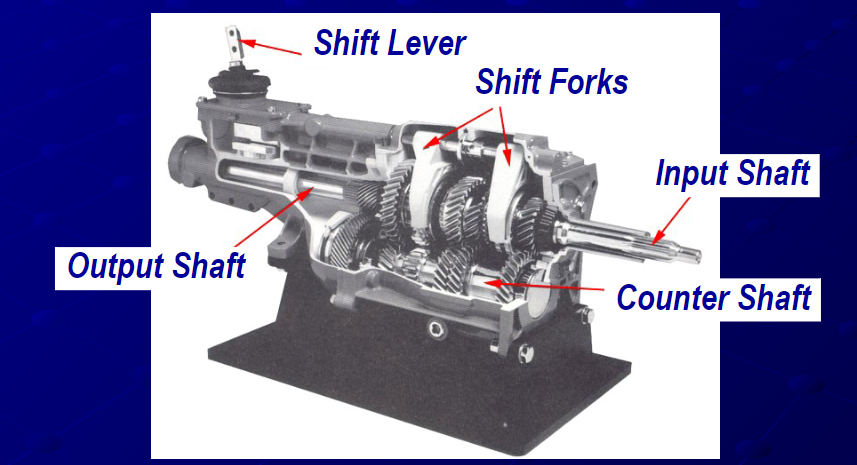
When the throw-out bearing is engaged, it removes the pressure from the clutch, stopping the transmission of power and allowing the driver to shift gears. Once the clutch is released, it re-engages with the flywheel and resumes receiving power from the crankshaft. In an automatic transmission, gear ratios change automatically as the vehicle moves, enabling the driver to select from various speeds suited to their current needs.

Inside the transmission, shift forks move gears along the input shaft and the countershaft. The input shaft connects to the engine, while the countershaft connects to the output shaft, which ultimately drives the wheels. This system allows the driver to select the appropriate gear for the speed and conditions, giving them a more direct and engaging driving experience.
Is manual or automatic better?
Despite the growing popularity of automatic cars, many people still prefer manual transmissions. Over the past two decades, increasing environmental concerns have driven research efforts to develop vehicles with greater efficiency and lower emissions. Consumers demand high performance and comfort without compromising on cost, making AMT a suitable solution as it balances performance, comfort, and efficiency while minimizing costs.
AMT combines the benefits of manual and automatic transmissions, utilizing existing manufacturing facilities to reduce production costs, improve efficiency, and have fewer moving parts. Manual transmissions offer the highest efficiency at 96.2 percent, while CVTs and automatic transmissions have efficiencies of around 84 percent and 86 percent, respectively. AMT matches the efficiency of manual transmissions while providing additional benefits.
In essence, automatic transmissions are easier to use and more comfortable for the driver. Whereas manual transmissions are typically less expensive and provide a more hands-on driving experience. A very small fraction of the US population knows how to drive a manual. As a result, your car will be safer from car theft since most people can’t drive it.
What are the disadvantages of manual transmission?
Manual transmissions have several disadvantages. They can become tiresome to use in heavy traffic due to the constant need for shifting. There’s also a steep learning curve, as it requires practice to master the coordination between the clutch and the gear lever. Driving on hills with a manual transmission demands precise control to avoid stalling or rolling back. As a result, manual transmissions are often hard to find, and only a limited number of vehicles offer them nowadays.
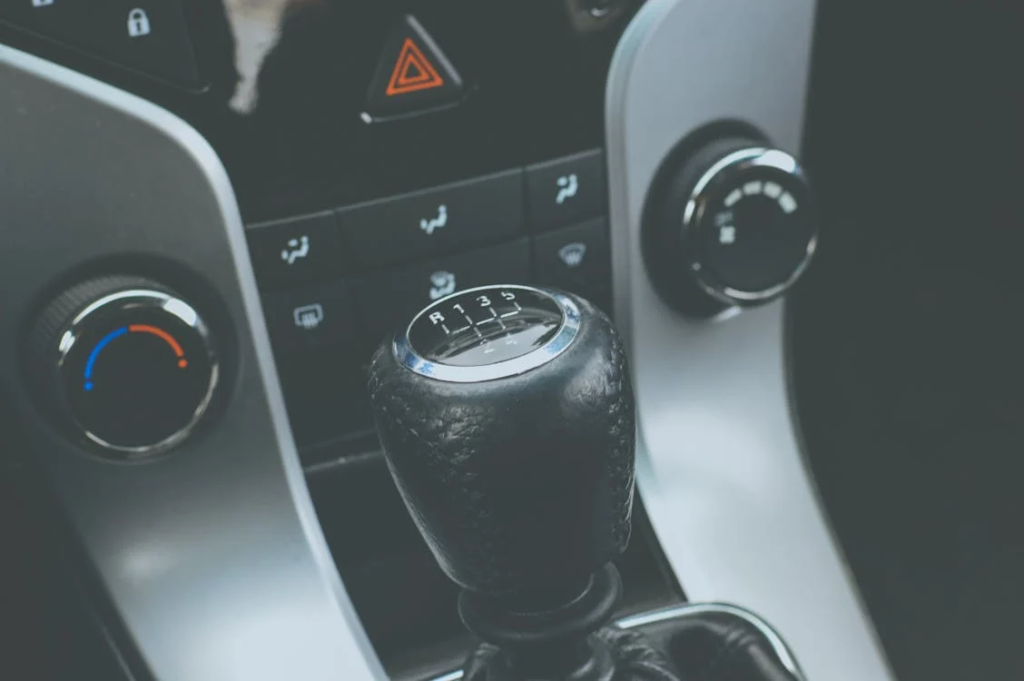

What percent of Americans can drive manually?
According to U.S. News and World Report, only about 18% of American drivers are capable of driving a manual transmission. This involves using the clutch pedal and stick shift.
Automatic Transmission
An Automated Manual Transmission (AMT) is a semi-automatic system where gear shifts are performed using electro-mechanical or hydraulic actuators. The AMT’s computerized control system determines when to shift gears and uses actuators to execute the shifts, essentially automating the process of a manual transmission.
It accomplishes this by leveraging a gear-shifting map in addition to sensing engine and wheel speed, using either mechanical or electronic control systems. Inside the automatic transmission, there is a complex system of gears known as a planetary gear set. This allows for the various gear ratios needed for different driving conditions.
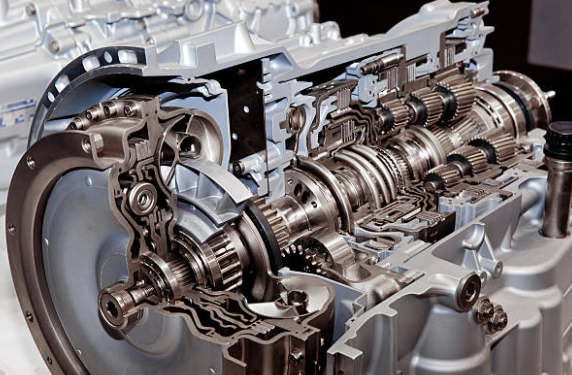
A popular example is the ZF five-speed automatic transmission. This type of transmission typically includes an overdrive (OD) mode for improved fuel efficiency at higher speeds. Automatic gearboxes utilize a torque converter instead of a clutch to transmit power from the engine to the transmission.
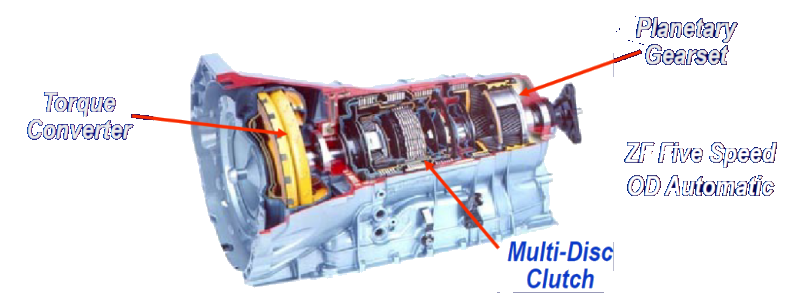
Numerous transmissions, particularly those designed for transportation, feature multiple gear ratios that can be changed while the vehicle is in motion. These various ratios are employed to align the range of input speeds (such as engine rpm) with the desired output speed (such as vehicle speed) needed for specific driving conditions.
Why do automatic transmissions need a torque converter?
Unlike a manual transmission’s clutch, the automatic transmission incorporates a torque converter. The torque converter’s role is to transmit power from the engine to the transmission system. It absorbs the engine’s energy when the vehicle is idling or stationary, preventing stalling. Issues with the torque converter can lead to erratic vehicle behavior.
How does an automatic transmission shift gears?
As the car moves forward, the transmission’s hydraulic and electronic systems detect the vehicle’s speed relative to the engine speed, causing the transmission to automatically shift gears. In a traditional automatic transmission, the hydraulics within the system sense these speed changes.
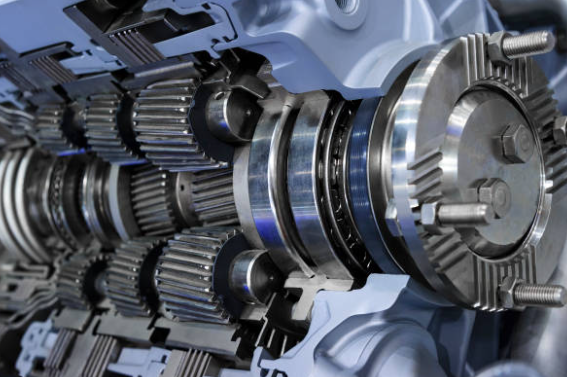
The most prevalent type of automatic transmission uses hydraulic power to shift gears. This system combines a torque or fluid coupling converter with a planetary gear set to deliver the necessary range of gears for the vehicle.
What controls the shifting in an automatic transmission?
The shifting process in an automatic transmission relies on an electro-hydraulic control system, which consists of two components: the electronic control system and the hydraulic actuation system.

How many planetary gear sets are available in the automatic transmission?
Inside the ten-speed transmission, there are four planetary gear sets and six shift elements. Among these shift elements, two are brakes (bands for the ring gears), and four are clutches that couple and decouple the sun and planet gears.
Is CVT better than automatic?
Unlike traditional automatic transmissions, a continuously variable transmission (CVT) uses a belt to provide an infinite combination of gear ratios. A semi-automatic transmission system features a clutch similar to a manual type, but it is controlled either electrically or hydraulically. CVTs enhance efficiency by enabling the engine to operate more frequently within its optimal efficiency “sweet spot.” However, CVTs come with their own set of drawbacks.
Transaxle
Transaxles combine the functions of a transmission and final drive into a single integrated assembly. This design is common in front-wheel-drive and some rear-engine vehicles. Power from the transaxle moves to a “con-vel” joint, which then transfers it to the wheels. One example of a transaxle is the Hydra-Matic 4T40-E/4T45-E, a four-speed automatic transaxle used in a variety of vehicles. The integration of the transmission and final drive into a single unit helps save space and weight, making transaxles popular in many modern vehicle designs.
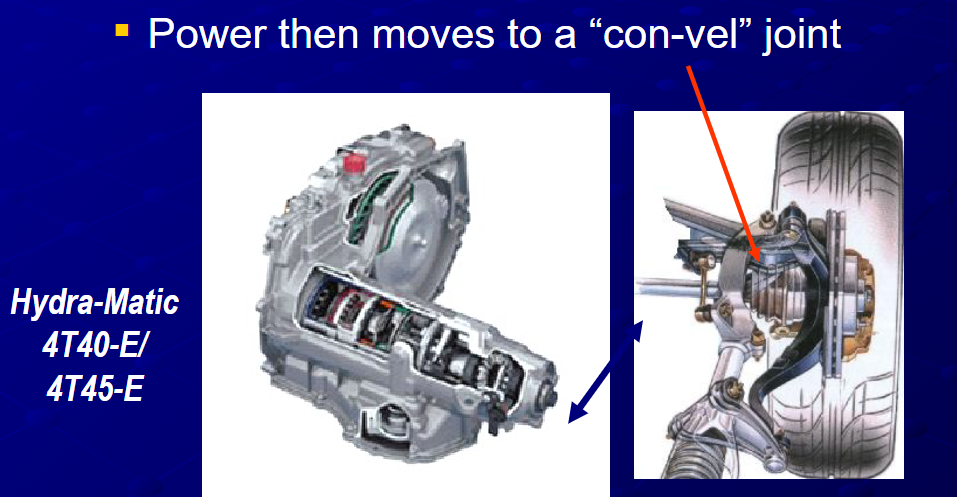
What is the role of the transaxle?
Its primary function is to transfer power from the engine to the drive wheels of a vehicle, especially when these wheels are located at the same end as the engine. Transaxles can be mechanical, hydraulic, or electric, and they find application in a wide range of vehicles such as passenger cars, sports cars, and commercial vehicles.
What does an automatic transaxle do?
Automatic transaxles consist of several components, including the torque converter, planetary gear set, hydraulic control unit, and valve body. The hydraulic control unit and valve body collaborate to regulate gear shifts according to the vehicle’s speed and engine load.
Conclusion
In conclusion, automotive transmissions play a critical role in the efficiency, performance, and driving experience of vehicles today. Whether manual or automatic, each type offers distinct advantages and considerations, influencing everything from fuel economy and maintenance costs to driver preference and vehicle design. As technology continues to advance, with innovations like hybrid and electric drivetrains emerging, the future of automotive transmissions promises further evolution toward greater efficiency and sustainability. Understanding the nuances of these systems empowers drivers and enthusiasts alike to make informed choices that align with their needs and the demands of modern motoring.