SAE J1516 – Accommodation Tool Reference Point
The following is a summary of SAE J1516.
Scope
Reference lines have been created to guide the positioning of driver workspace accommodation tools within vehicle space, based on horizontal reference points tied to H-point height (H30). For Class A vehicles (H30 under 405 mm and steering wheel diameter under 450 mm), a single reference line is available for a balanced male-to-female driver ratio (50:50). For Class B vehicles (H30 between 405 and 530 mm, steering wheel diameter between 450 and 560 mm, and treadle-type pedals), three reference lines are available, allowing for varied male-to-female ratios: 50:50, 75:25, and 90:10 to 95:5. Separate procedures for Class A and Class B vehicles account for the distinct design needs of each category.
References
The following SAE publications are integral to this specification, with the latest versions applied unless stated otherwise. Key references include:
- SAE J941: Motor Vehicle Driver’s Eye Range
- SAE J1052: Driver and Passenger Head Position
- SAE J1100: Vehicle Dimensions
- SAE J1517: Driver Selected Seat Position
- SAE J1521: Truck Driver Shin-Knee Position for Clutch and Accelerator
- SAE J1522: Truck Driver Stomach Position
Additional studies include research on truck driver anthropometrics and workspaces, such as the works by Philippart et al. (1984) and Sanders (1983, 1984). These publications are available from SAE, Warrendale, PA.
Definitions
In addition to definitions from SAE J1100 (e.g., H-point, H30, W9, AHP, and SgRP), vehicles are classified by specific H-point heights (H30) and steering wheel diameters (W9):
- Class A Vehicles: Defined by H-point heights (H30) below 405 mm and steering wheel diameters (W9) below 450 mm, covering passenger cars, multipurpose vehicles, and vans.
- Class B Vehicles: Defined by H-point heights (H30) between 405 and 530 mm and steering wheel diameters (W9) between 450 and 560 mm, including heavy trucks, some medium-duty trucks, and some buses.
Key definitions and equations for Class A vehicles include:
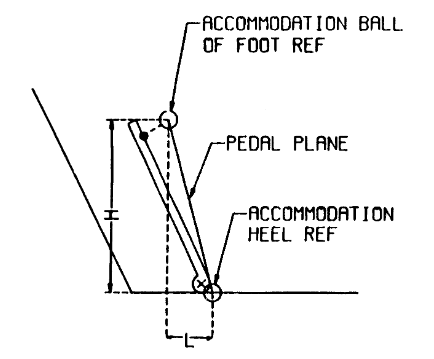
- Accommodation Tool Reference Line: This 2D side-view curve defines a horizontal reference point based on H-point height (H30) for driver workspace accommodation. The reference line, suitable for a 1:1 male-to-female ratio, is calculated with:
x = 793.7 – 0.903387z + 0.00225518z2
where (x) is the horizontal reference location in mm from the accommodation ball of foot reference, and (z) is the H-point height above the heel reference (H30) in mm. - Pedal Plane Angle: The angle (( \theta )) between the pedal plane and horizontal floor, derived from the manikin’s geometry (95th percentile leg links and 87-degree foot angle). The angle is calculated as:
θ = 78.96 – 0.15z + 0.0173z2
where (z) is the height of the H-point above the accelerator heel point in cm. - Ball of Foot: Located 203 mm from the accelerator heel point, tangent to the bottom of the manikin’s shoe at the ball of foot.
These equations and definitions provide essential guidance for positioning driver workspace tools in Class A vehicles based on ergonomic considerations.
The 95th Percentile Selected Seat Position Curve defines the driver-selected seat position relative to the ball of foot reference, based on H-point height (H30) for accommodating the 95th percentile driver. It is calculated as:
x = 913.7 – 0.672316z + 0.0019553z2
where (x) is the 95th percentile H-point position in mm, and (z) is the H-point height above the accelerator heel point (H30).
For Class B Vehicles, three Accommodation Tool Reference Lines are provided to adjust for varying male-to-female ratios among drivers:
- 50:50 Ratio:
x = 798.74 – 0.446z - 75:25 Ratio:
x = 822.44 – 0.460z - 90:10 to 95:5 Ratio:
x = 855.31 – 0.509z
Each line gives the horizontal reference point (x) as a function of H-point height (z) for driver workspace tools.
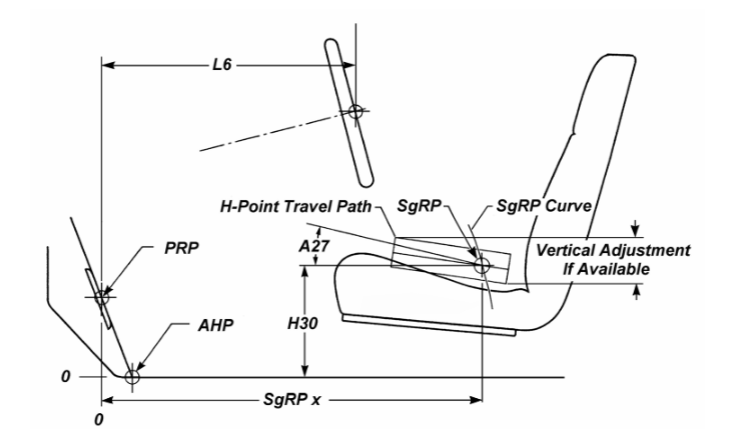
The Accommodation Heel Reference Point marks the pedal plane intersection with the floor covering below the accelerator pedal, creating horizontal and vertical reference planes essential for positioning Class B workspace tools. The Pedal Plane angle also helps set the pedal’s orientation based on the driver’s foot positioning, adapting for manikin geometry in the workspace.
Background
Previously, manufacturers used the seating reference point (SgRP) for driver workspace tools, but inconsistencies among vehicle models led to variations in accommodation. To standardize this, reference lines for driver workspace were created for Class A and Class B vehicles based on driver seating data.
Data from fourteen studies were used for Class A vehicles (passenger cars, vans, etc.). The median H-point location, representing driver seating positions across different vehicle types, was calculated and modeled with a second-degree polynomial to create a consistent reference line for a 50:50 male-to-female driver population.
Workspace data from truck cab studies were used for Class B vehicles (trucks and heavy vehicles with treadle pedals). Linear equations were derived for H-point locations for driver populations with male-to-female ratios of 50:50, 75:25, and 90:10 to 95:5, establishing separate reference lines for each mix.
Description
Equations establish horizontal reference points in vehicle space based on H-point height, allowing consistent placement of driver workspace tools. For Class A vehicles (1:1 male-to-female driver population), a second-degree equation defines a reference line using the ball of foot and heel reference points. For Class B vehicles, three linear equations define reference lines for driver populations with varying male-to-female ratios (50:50, 75:25, and 90-95% males). Reference lines in both vehicle classes are positioned relative to specific side view planes, with Class A using both foot reference points, while Class B relies solely on the heel reference.
Table 1 provides reference data for positioning the accommodation heel and ball of foot points in Class A vehicles. The table specifies the horizontal (L) and vertical (H) distances between these points, allowing for direct setup of the pedal plane without needing to calculate the pedal plane angle (θ). This simplifies defining the accommodation tool reference line in vehicle space.
Locating Procedures
Class A and Class B vehicles have distinct procedures to locate the accommodation tool reference line based on H-point height and pedal configuration.
Class B Vehicles: For treadle pedals, define the pedal plane and angle (θ), then locate the heel reference point where the plane meets the floor covering. For design, adjust for population mix when locating the tool reference line.
Class A Vehicles: Use a triangle with values from Table 1 (L and H) to define the accommodation heel and ball of foot reference points along a pedal plane angle (θ). Adjust for pedal shape and pivot as needed. For treadle pedals:
If pedal angle < θ, pivot until the ball of the foot point contacts the pedal.
If pedal angle > θ, set the ball of foot reference point at pedal contact, regardless of heel contact.
Table 1—5.2 APPLICATION TABLE:
| Chair Height (Z) mm | 95% H-Point Aft of Ball of Foot (X) mm | Ball of Foot Length to Heel Point (L) mm | Ball of Foot Height Above Heel Point (H) mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 961.4 | 50.0 | 196.7 |
| 105 | 962.7 | 50.9 | 196.5 |
| 110 | 964.0 | 51.8 | 196.3 |
| 115 | 965.2 | 52.7 | 196.0 |
| 120 | 966.2 | 53.7 | 195.8 |
| 125 | 967.2 | 54.7 | 195.5 |
| 130 | 968.1 | 55.7 | 195.2 |
| 135 | 968.8 | 56.7 | 194.9 |
| 140 | 969.5 | 57.8 | 194.6 |
| 145 | 970.1 | 58.9 | 194.3 |
| 150 | 970.6 | 60.0 | 193.9 |
| 155 | 970.9 | 61.1 | 193.6 |
| 160 | 971.2 | 62.3 | 193.2 |
| 165 | 971.4 | 63.5 | 192.8 |
| 170 | 971.5 | 64.7 | 192.4 |
| 175 | 971.5 | 66.0 | 192.0 |
| 180 | 971.4 | 67.3 | 191.5 |
| 185 | 971.2 | 68.6 | 191.1 |
| 190 | 970.9 | 69.9 | 190.6 |
| 195 | 970.5 | 71.2 | 190.1 |
| 200 | 970.0 | 72.6 | 189.6 |
| 205 | 969.4 | 74.0 | 189.0 |
| 210 | 968.7 | 75.5 | 188.5 |
| 215 | 967.9 | 76.9 | 187.9 |
| 220 | 967.0 | 78.4 | 187.3 |
| 225 | 966.0 | 79.9 | 186.6 |
| 230 | 964.9 | 81.4 | 186.0 |
| 235 | 963.7 | 83.0 | 185.3 |
| 240 | 962.4 | 84.5 | 184.6 |
| 245 | 961.1 | 86.1 | 183.8 |
| 250 | 959.6 | 87.7 | 183.1 |
| 255 | 958.0 | 89.4 | 182.3 |
| 260 | 956.3 | 91.0 | 181.5 |
| 265 | 954.6 | 92.7 | 180.6 |
| 270 | 952.7 | 94.4 | 179.7 |
| 275 | 950.7 | 96.1 | 178.8 |
| 280 | 948.7 | 97.8 | 177.9 |
| 285 | 946.5 | 99.6 | 176.9 |
| 290 | 944.2 | 101.3 | 175.9 |
| 295 | 941.9 | 103.1 | 174.9 |
| 300 | 939.4 | 104.9 | 173.8 |
| 305 | 936.9 | 106.7 | 172.7 |
| 310 | 934.2 | 108.5 | 171.6 |
| 315 | 931.5 | 110.4 | 170.4 |
| 320 | 928.6 | 112.2 | 169.2 |
| 325 | 925.7 | 114.1 | 167.9 |
| 330 | 922.6 | 115.9 | 166.6 |
| 335 | 919.5 | 117.8 | 165.3 |
| 340 | 916.3 | 119.7 | 163.9 |
| 345 | 912.9 | 121.6 | 162.5 |
| 350 | 909.5 | 123.5 | 161.1 |
| 355 | 906.0 | 125.5 | 159.6 |
| 360 | 902.3 | 127.4 | 158.1 |
| 365 | 898.6 | 129.3 | 156.5 |
| 370 | 894.8 | 131.2 | 154.9 |
| 375 | 890.9 | 133.2 | 153.2 |
| 380 | 886.8 | 135.1 | 151.5 |
| 385 | 882.7 | 137.0 | 149.8 |
| 390 | 878.5 | 139.0 | 148.0 |
| 395 | 874.2 | 140.9 | 146.1 |
| 400 | 869.8 | 142.8 | 144.2 |

Wow! Thank you! I always needed to write on my blog something like that. Can I include a part of your post to my blog?
Of course!
yeah bookmaking this wasn’t a bad determination great post! .