Similar Posts

Dipole and Quadrupole
In electromagnetism, the concepts of dipoles and quadrupoles play a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of electric and magnetic fields. Though similar in some respects, these fundamental systems exhibit distinct behaviors and characteristics that influence a wide range of physical phenomena. Whether you’re studying electric charges, magnetic fields, or even sound waves, the properties…
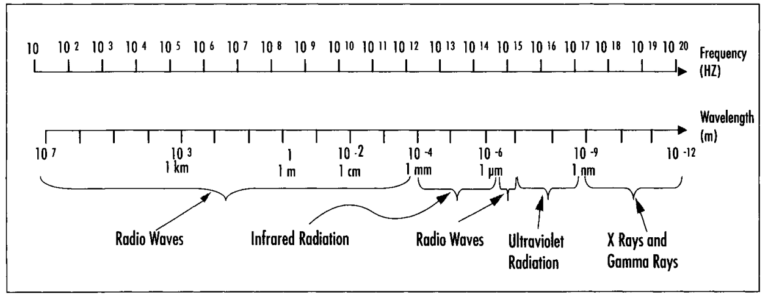
Sound and Electromagnetic Waves
Waves are fundamental to our understanding of the physical world, carrying energy and information across vast distances. Among the many types of waves, electromagnetic waves stand out for their versatility and profound impact on science and technology. These waves, including visible light to X-rays and radio waves, are essential to countless applications in daily life,…

Why AC circuits are cooler than DC circuits: A beginner’s guide
Introduction Alright, so first things first – let’s talk about what AC and DC circuits are. AC stands for Alternating Current, and it’s the boss when it comes to powering most of the stuff around us, All of the 120V outlets in your house are AC. On the other hand, DC stands for Direct Current…
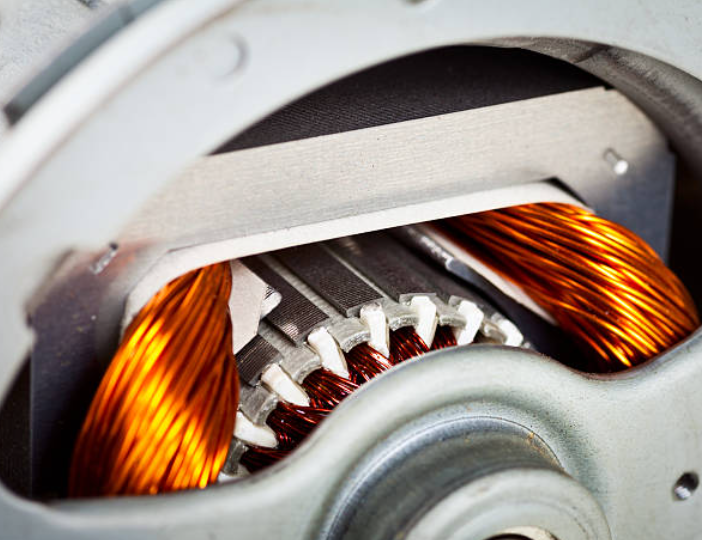

DC Motor Design
A DC motor utilizes direct current (DC) to generate mechanical force, commonly relying on magnetic forces produced by currents in its coils. Nearly all DC motors incorporate an internal mechanism, whether electromechanical or electronic, to periodically alter the direction of current within the motor. DC motors were initially widely adopted as they could be powered…
The Power of a AC Motor
What are AC Motors? An AC motor or alternating current electric motor is powered by alternating current (AC) and typically comprises two main components. The outer stator contains coils that receive AC to create a rotating magnetic field, while the inner rotor, connected to the output shaft, generates another rotating magnetic field. The rotor’s magnetic…
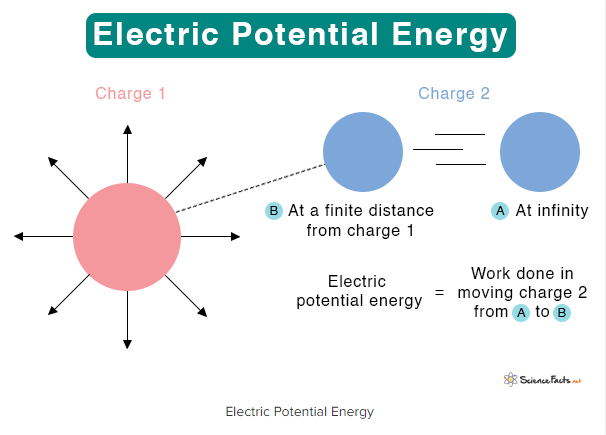
Electric Potential and Energy
Hey everyone! Today, we are going dive into the fundamental concepts from Physics 2, covering electric potential, energy, and the relationships governing charged particles. These principles are crucial for understanding electrostatics and provide a foundation for advanced applications in physics and engineering. What is meant by electric potential energy? Okay, so first things first –…
