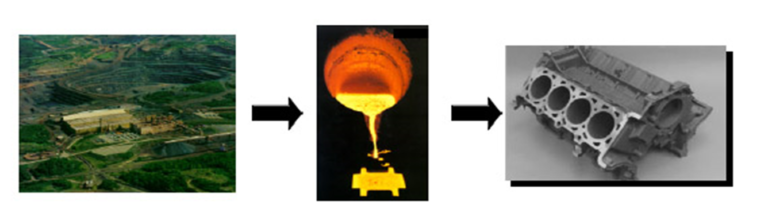
The Automotive Industry
The automotive industry encompasses all companies and activities involved in producing motor vehicles. The industry’s main products are passenger cars and light trucks, including pickups, vans, and sport utility vehicles. Commercial vehicles, like delivery trucks and 18- 18-wheelers (often called semis), are secondary to the industry.
The term “automotive” originates from the Greek word “autos” (self) and the Latin word “motivus” (of motion). Thus automobile refers to any self-powered vehicle aka not require a horse. This term was first suggested by Elmer Sperry (1860–1930) and began to be used to describe automobiles in 1898. The automobile industry ranks among the world’s largest industries by revenue. Contributing to 16% of France’s revenue and as much as 40% in places like Slovakia.
What do you mean by the automotive industry?
The automotive industry includes companies and organizations involved in designing, developing, manufacturing, selling, repairing, and modifying motor vehicles.
What are the largest automotive companies in the world?
The largest automotive companies include SAIC Motor, BMW Group, Honda, General Motors, Ford, Daimler, Toyota, and Volkswagen Group. These industry giants are renowned for their extensive global reach, diverse product lines, and significant contributions to automotive innovation/manufacturing.

Who are the top automotive suppliers?
The top automotive suppliers in the world include Bosch, which is the largest, and Denso, which remains the second largest. Other major suppliers include BASF SE, Mitsubishi Electric Corp, Hyundai Mobis Co. Ltd, ZF, and Magna International Inc. These companies play crucial roles in providing essential components and technologies that drive the global automotive industry.
Automotive Industry History
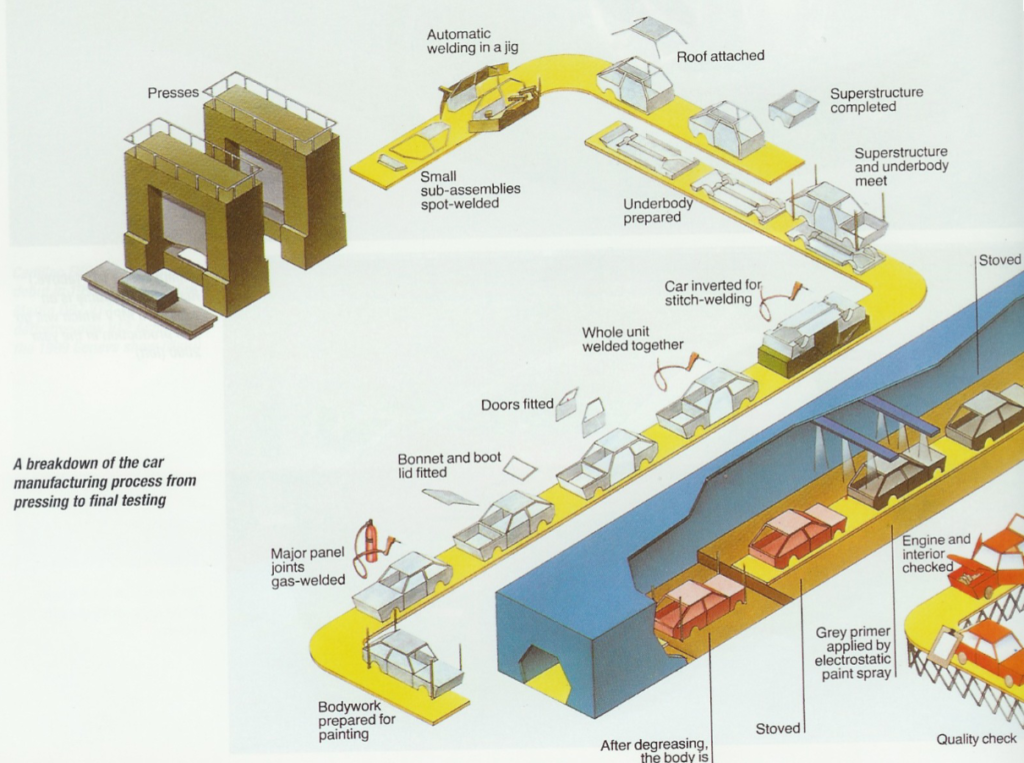
The automotive industry began in the 1860s with numerous manufacturers developing horseless carriages. Initially, cars were manually assembled by human workers. Over time, the process evolved from stationary assembly to an assembly line system with specialized engineers. By the 1960s, robotic equipment was introduced. Today, most cars are primarily assembled by automated machinery.
For many decades, the United States led the world in automobile production. The Detroit Big Three—General Motors, Ford, and Chrysler—were the largest auto manufacturers for a time. GM and Ford remained the two largest until the mid-2000s.
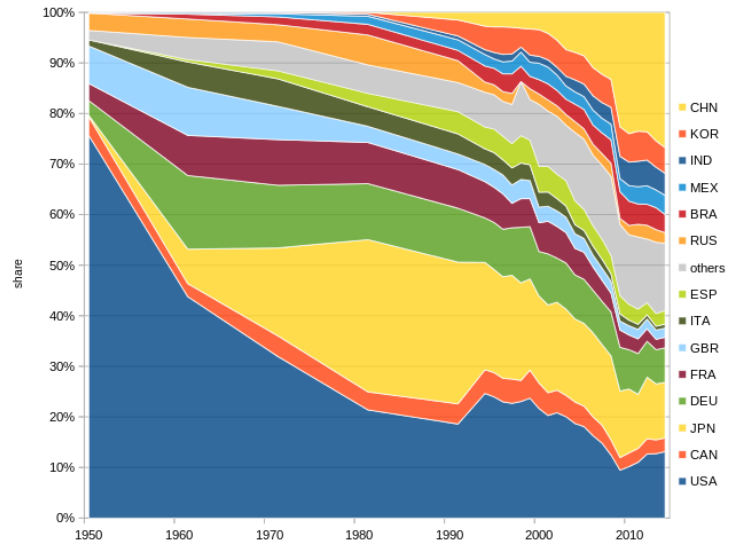
In 1929, before the Great Depression, the U.S. produced over 90% of the world’s 32 million automobiles. Post-1945, the U.S. accounted for about three-quarters of global auto production. Japan overtook the U.S. in 1980, and again in 2006 and 2007, while China became the top producer in 2009. By 2017, China produced over 29 million vehicles, marking the largest margin over the U.S.
Why is the automotive industry so important?
The automotive industry in the United States is a crucial driver of economic growth, deeply interconnected with various aspects of the country’s industry and culture. With over 1.7 million people employed, the auto industry is a significant contributor to the economy. It also heavily relies on goods and services from other sectors.

Economical Impacts of the Automotive Industry
The economic impacts of the automotive industry are profound and far-reaching. A robust auto manufacturing sector is essential for a healthy U.S. economy. The automotive industry supports a total of 9.7 million American jobs, which constitutes about 5 percent of private-sector employment. This includes direct, indirect, and induced positions, leading to $702 billion in paychecks for millions of workers nationwide.

Each job in auto manufacturing creates nearly 10.5 additional positions in various industries across the economy. This multiplier effect demonstrates the industry’s significant role in driving economic activity. Auto manufacturing injects more than $1 trillion into the economy annually through the sales and servicing of vehicles.
Furthermore, the industry contributes nearly $280 billion annually in federal, state, and local tax revenues. This includes over $69 billion in federal income taxes and $79 billion in state revenue, underscoring its importance to government finances. Given these substantial contributions, it’s no surprise that politicians are keen on maintaining and promoting local automotive manufacturing.
Environmental Impacts on the Automotive Industry
The environmental impacts of the automotive industry are significant and multifaceted. Cars consume a lot of energy even before they hit the road. The production process of automobiles leaves a substantial environmental footprint. Cars require many engineering materials like steel, rubber, glass, plastics, and paints, all of which require considerable energy and resources.
The global automotive industry is also a significant water consumer. It is estimated that 180,000 liters (39,000 gallons) of water is needed per car. Key processes that consume large volumes of water include surface treatment, painting, coating, washing, cooling, air-conditioning, and boiler operations, excluding component manufacturing. Paintshop operations are particularly water-intensive because equipment using water-based products also requires water for cleaning.
What is the Tesla Gigafactory controversy?
Tesla opened its Gigafactory near Berlin in 2022 and has since announced a significant expansion to boost its battery storage capacity. However, these plans have sparked outrage among environmental activists. Activists are upset that the expansion would involve clearing large areas of nearby forests

Later that year Tesla’s Gigafactory Berlin faced legal challenges due to droughts and declining groundwater levels in the region. Brandenburg’s Economy Minister, Joerg Steinbach, stated that while the initial water supply was sufficient, expansion of the site would require more. The factory’s water consumption would nearly double in the Gruenheide area. With 1.4 million cubic meters contracted annually from local authorities, enough for a city of around 40,000 people. Steinbach mentioned that authorities plan to drill for more water and outsource additional supplies if necessary.
In March of 2024, Tesla had to shut down and scale back production at Gigafactory Berlin for significant reasons. The shutdown was due to an arson attack by self-proclaimed environmentalists, while the production reduction was caused by supply chain issues related to the Red Sea conflict.
How much do cars contribute to global warming?
Once on the road, the transport sector becomes one of the largest consumers of the world’s petroleum, contributing heavily to global greenhouse gas emissions. This sector is a major source of air pollution, with cars emitting substantial amounts of nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and particulate matter, all of which have detrimental effects on air quality and public health.
As a response to these environmental challenges, there has been a significant push towards more environmentally sustainable options, such as electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrids. These alternatives aim to reduce the environmental footprint of transportation by lowering emissions and relying less on fossil fuels, thus addressing both energy consumption and pollution issues associated with traditional automotive production and usage.
What is the largest automobile industry in the world?
China is the world’s leading vehicle producer, manufacturing over 21.4 million cars and 4.6 million commercial vehicles in 2021, totaling slightly more than 26 million vehicles.
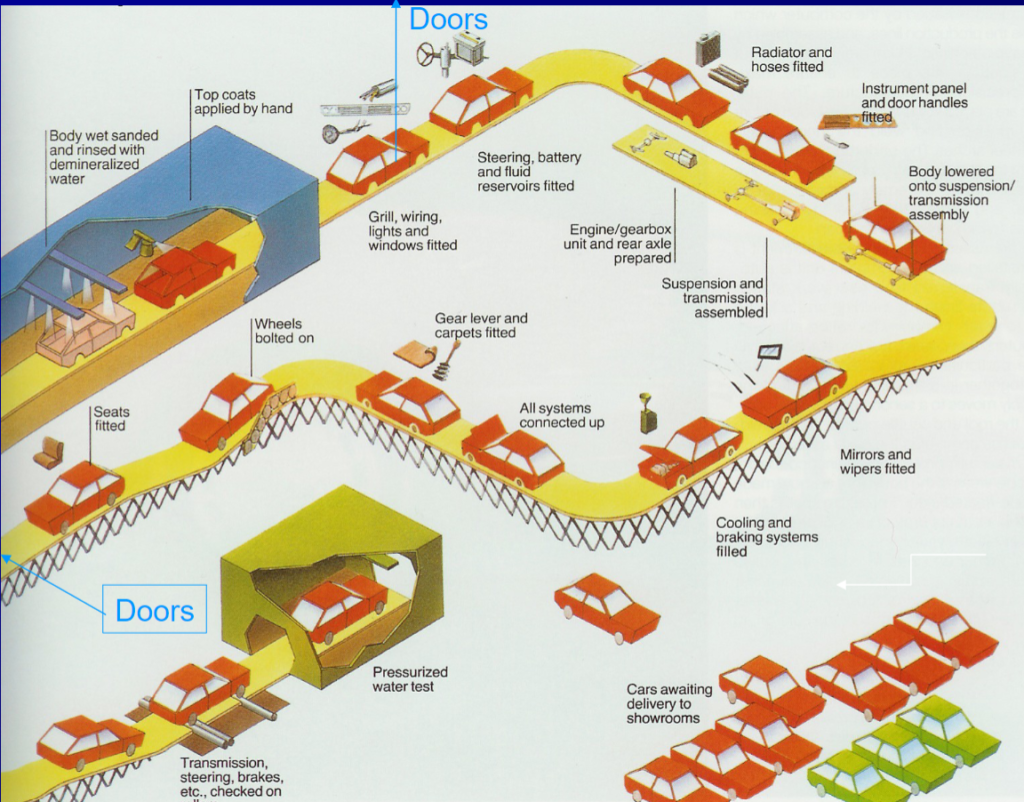
What are the top 3 car brands?
The top three U.S. car brands are assembled and distributed by the leading manufacturers in the U.S. market: Ford Motor Company, Toyota Motor Corporation, and General Motors (GM).
What states have car manufacturing plants?
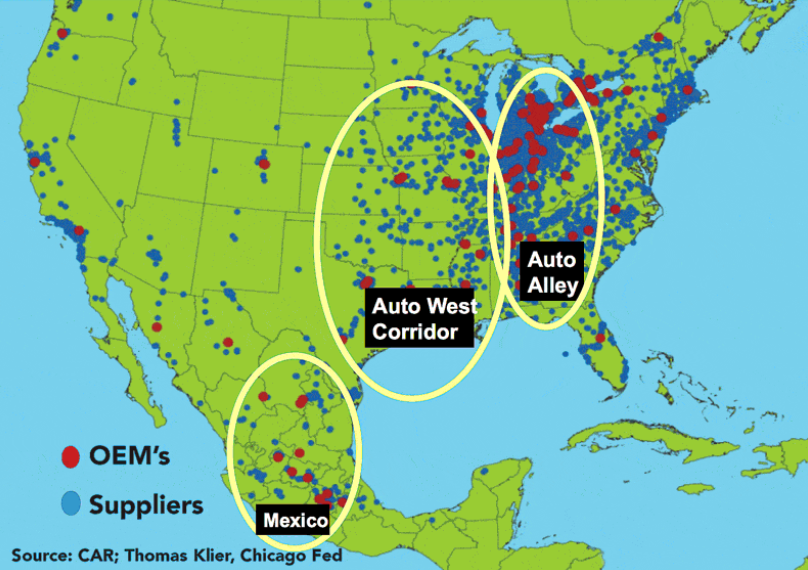
The states with car manufacturing plants are primarily located in the Midwest and South regions of the United States. Michigan in the Midwest has the highest concentration, with more than 950 auto manufacturing plants, including those for vehicles and auto parts. In the South, manufacturing plants are based in Georgia, Kentucky, Mississippi, North Carolina, West Virginia, Texas, Tennessee, and Alabama.
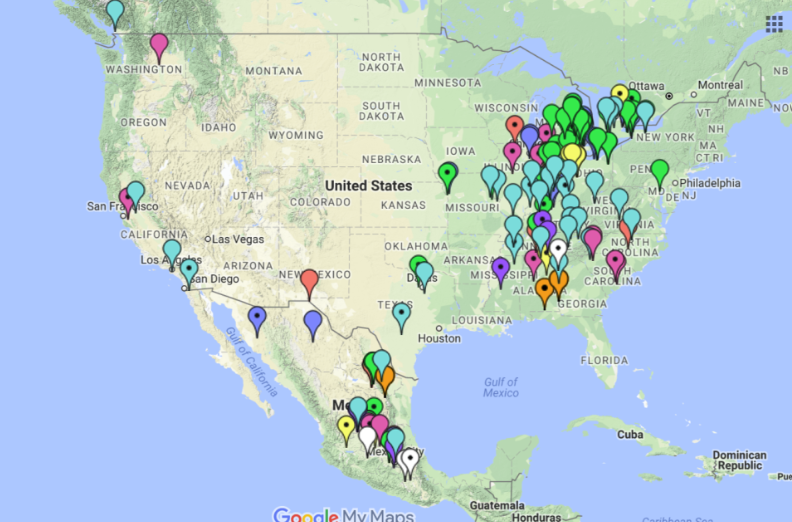
Auto Alley refers to the region encompassing both automobile suppliers and manufacturers. Suppliers are concentrated in the southern United States and northern Mexico, while manufacturers are primarily clustered in the northern U.S. Midwest, particularly Michigan, and parts of Canada. Supplies are transported from the south to the north for final assembly. This setup has prompted efforts to shift manufacturing to the south or suppliers to the north, but these efforts have yielded limited results.
Why did the automotive industry leave Detroit?
First of all, the development of the assembly line rendered many of Detroit’s multi-story downtown factories inefficient. Automakers needed more space for their new production methods, leading them to build more spacious factories in suburban areas. This shift resulted in a mass exodus from Detroit.
Second, the decline began in the 1960s when a building boom pushed people into the suburbs. This transition, where one ethnic group (whites) moved out and another (African Americans) moved in. This was only exacerbated by the racial riots in 1967, accelerating the exodus.

Third, by the 1970s, auto companies started moving factories to right-to-work states, which don’t require union representation. This move reduced United Automobile Workers (UAW) membership significantly as workers in these states opted out of joining the union, and companies increasingly automated operations.
Finally, generous worker benefits and declining product quality contributed to the downfall of the Big Three. Starting in the 1950s, automakers moved operations to Detroit’s suburbs and beyond to build larger, automated plants. They also opened plants in other states to be closer to customers and shifted production overseas to Mexico and Brazil to reduce costs assembly costs.

Detroit’s auto jobs diminished as the Big Three lost market share to foreign automakers starting in the 1970s. This was a result of the manufacturing edge automakers like Toyota had on the Big Three due to their innovative lean manufacturing technique. This allowed for their cars to be more fuel efficient and with higher quality than comparable American vehicles. These combined factors led to the automotive industry’s departure from Detroit, contributing to the city’s economic decline.
NAFTA as a Major Stimulus of Regional Integration
Before NAFTA was established in 1994, cross-border integration in the automotive industry between the U.S., Canada, and Mexico was already well underway. By the 1980s, all three major U.S. car manufacturers, General Motors, Chrysler, and Ford Motor Company, had set up car assembly plants in Mexico. Chrysler opened its first plant in Toluca, State of Mexico, in 1968, while General Motors established its first modern plant in Ramos Arizpe, Coahuila, in 1981. Ford Motor Company followed suit in 1981, opening plants in Chihuahua and Toluca, and then in 1986, in Hermosillo, Sonora, which is crucial to Arizona’s economy due to its proximity.

Since the mid-1960s, the maquiladora program in Mexico, along with special U.S. tariff provisions, allowed for duty-free import/export of U.S.-manufactured parts assembled in Mexico and returned to the U.S. parent companies. Although the U.S.-owned car assembly plants were not officially part of Mexico’s maquiladora sector, they enjoyed similar benefits and relied on it for parts and components. In 2006, the maquiladora sector and the auto industry in Mexico were combined into a single program known as IMMEX (Industria Manufacturera, Maquiladora y Servicios de Exportación).
NAFTA significantly boosted the automotive industry in Mexico, including car assembly and parts manufacturing plants. The Rule of Origin, one of NAFTA’s original provisions, attracted Asian and European car manufacturers seeking access to the U.S. market by establishing plants in Mexico. According to this rule, parts and components manufactured in Mexico (or in the U.S. or Canada) qualify as duty-free imports/exports within NAFTA countries.
Why does China produce the most cars?
Rapid urbanization, manufacturing growth, and the resulting job increases led to a significant rise in Gross National Income per capita, expanding the middle class. This growth boosted the middle-class population to approximately 63 million people or 5% of the total population.
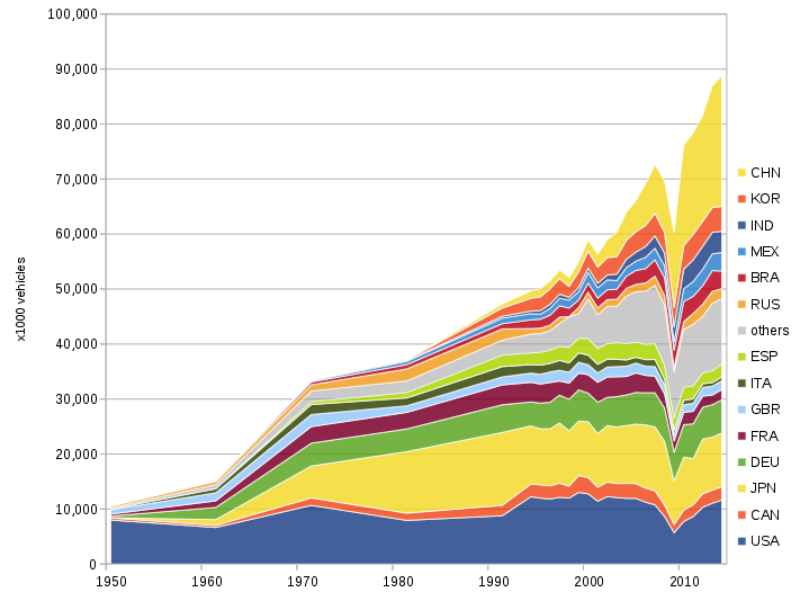
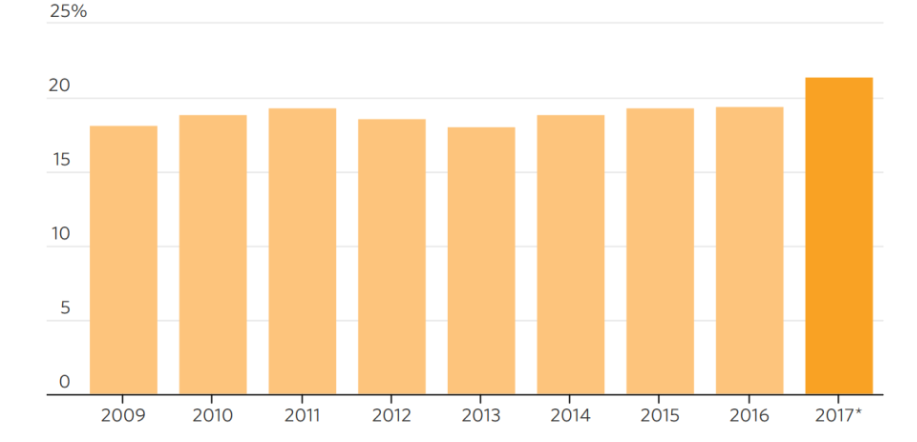
This expansion is strongly linked to China’s economic progress and the emergence of a larger middle class. More Chinese families are now able to purchase cars, resulting in a significant increase in sales. As a result, China’s automotive production skyrocketed from two million vehicles in 2000 to 29 million vehicles in 2017.
Conclusion
The automotive industry has undergone profound transformations over the decades, driven by technological advancements, economic shifts, and changing consumer preferences. From the early days of manual assembly to the highly automated processes of today, the industry has continually evolved to meet the demands of a global market. The rise of new manufacturing hubs, the impact of globalization, and the shift towards sustainable and electric vehicles are reshaping the landscape. Despite challenges, including economic downturns and competitive pressures, the industry’s resilience and adaptability ensure its ongoing significance. As it navigates the future, the automotive industry will continue to be a cornerstone of economic development, innovation, and employment across the world.