Why AC circuits are cooler than DC circuits: A beginner’s guide
Introduction
Alright, so first things first – let’s talk about what AC and DC circuits are. AC stands for Alternating Current, and it’s the boss when it comes to powering most of the stuff around us, All of the 120V outlets in your house are AC. On the other hand, DC stands for Direct Current which is the electricity you get from batteries. But, hey, why are AC circuits cooler than DC circuits? Well, you’re about to find out, my friends!

What is an AC circuit?
An Alternating Current (AC) circuit is a type of electric circuit that circuits powered by an alternating source, either voltage or current. AC is a form of current that changes its direction and magnitude periodically, unlike direct current (DC) which flows in one direction only. AC circuits are commonly used in household appliances, power transmission and distribution, and electronic devices. The main components of an AC circuit are a voltage source, a load, and optionally some passive elements such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors.

Understanding AC and DC
Imagine this: AC is like a dance party, where everyone’s moving and grooving. It’s called alternating because the flow of electricity constantly changes direction, just like a surfer riding waves. On the other hand, DC is more like a one-way street, where the electricity flows in a straight line.
The Power of Oscillation
Now, here’s the real magic of AC – oscillation! Picture this – AC current is like a wave at the beach, going up and down, up and down. This constant change in direction allows electricity to travel long distances without losing much energy. That’s one big reason why AC is the king of power transmission.

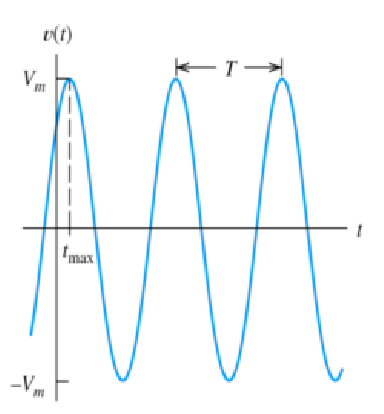
What are the characteristics of a sinusoidal wave?
A sinusoidal wave is a smooth, repetitive oscillation with distinct characteristics. It follows a sine function, displaying a periodic rise and fall. The wave has a specific frequency, amplitude period, and phase, making it ideal for representing alternating current (AC) in electrical circuits.
- Vm is the peak value
- w is the angular frequency in radians per second
- theta is the phase angle
- T is the period
Advantages of AC Circuits
Imagine trying to send power from one city to another using DC. It’s like trying to carry a heavy bag on a long journey – you get tired and drop stuff along the way. Well, that’s what happens to DC when it travels long distances; it loses a ton of energy. But AC, oh boy, it’s a rockstar at this! It can go from city to city with minimal energy loss, thanks to its oscillating moves.
AC in Our Daily Lives
You won’t believe how much AC has revolutionized our lives! From the moment you wake up and turn on the lights, to the moment you charge your phone before hitting the sack – it’s all AC electricity! This awesome current powers our homes, appliances, computers, and even electric cars.
How to solve a AC circuit
To solve an AC circuit, analyze its components using phasor diagrams and complex numbers to find voltage, current, and impedance values at steady-state conditions.
What is the formula for power in an AC circuit?
Below is the list of equation you will need when solving AC circuit problems
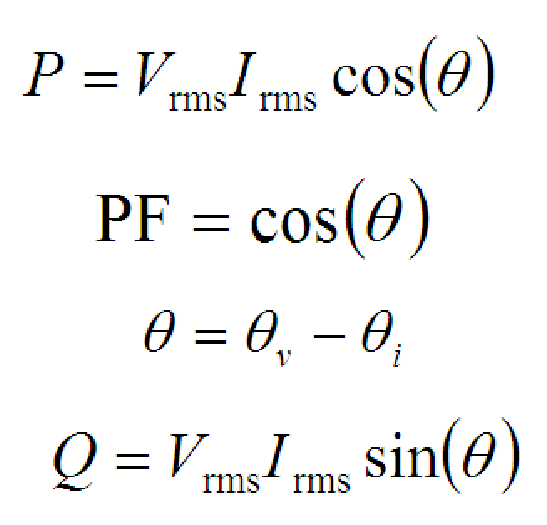
Sample Problem
Find the power delivered to a 50 ohm resistance by this voltage source v(t) =100cos(100t).
Solution:
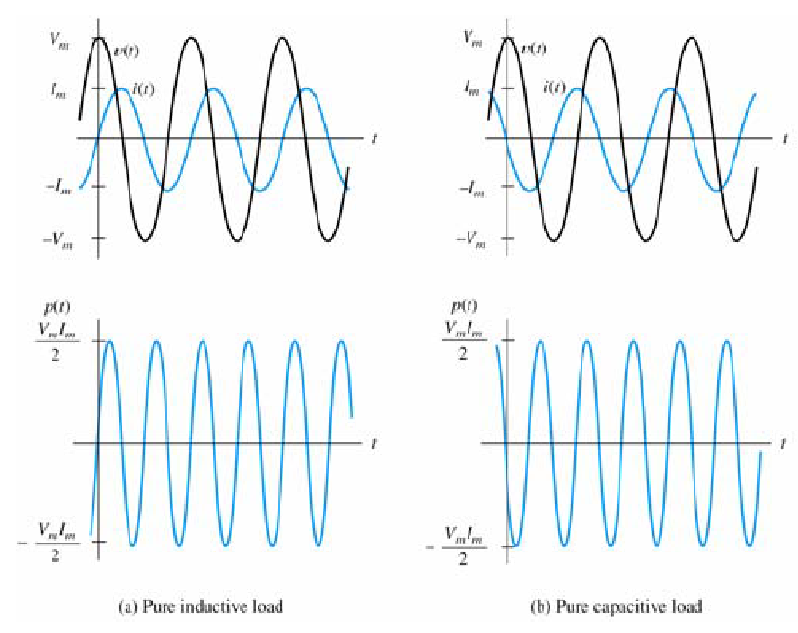
Voltage, current, and power for inductive and capacitive loads in an AC circuit:
What is steady state AC analysis?
Steady-state AC analysis is a method used to analyze alternating current (AC) circuits when they have reached a stable operating condition. In this analysis, the transient effects have settled, and the currents and voltages have stabilized at constant values. Engineers and researchers solve steady-state AC circuits using phasors and complex impedances to determine circuit performance, voltage and current magnitudes, power distribution, and to determine load impedances for maximum power transfer. It simplifies the complex dynamic behavior of AC circuits, providing essential insights for practical applications.
What is the root mean square?
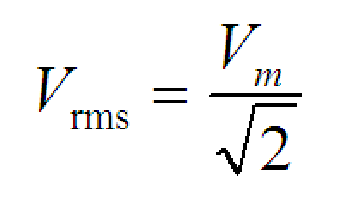
Root Mean Square (RMS) is a mathematical measure used to find the effective or equivalent value of a varying quantity, like voltage or current in an AC circuit. The RMS value for a sinusoid is the peak value divided by the square root of two. This is not true for other periodic waveforms such as square waves or triangular waves.
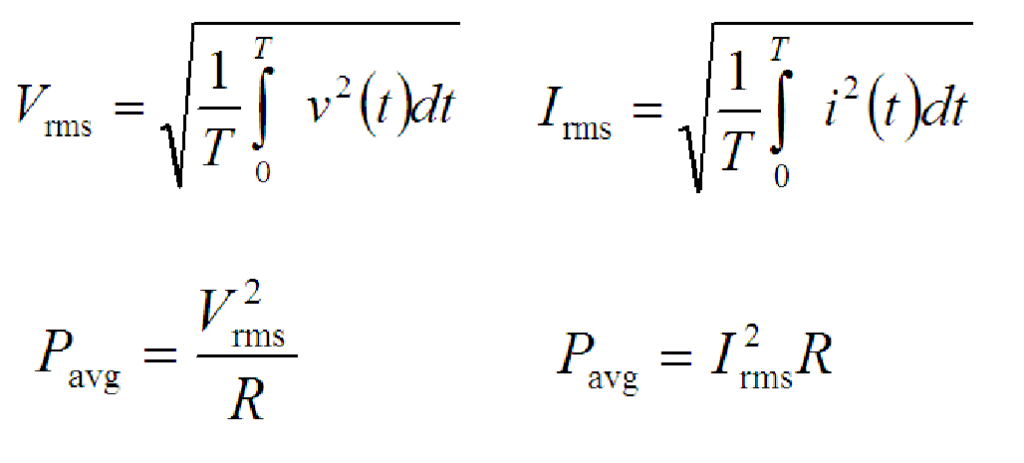
What Is Apparent Power?
In an AC circuit, the product of the root mean square voltage and current is called apparent power. When the impedance is a just real, the apparent power is the same as the true power. But when reactance exists (complex impedance), the apparent power is greater than the true power.
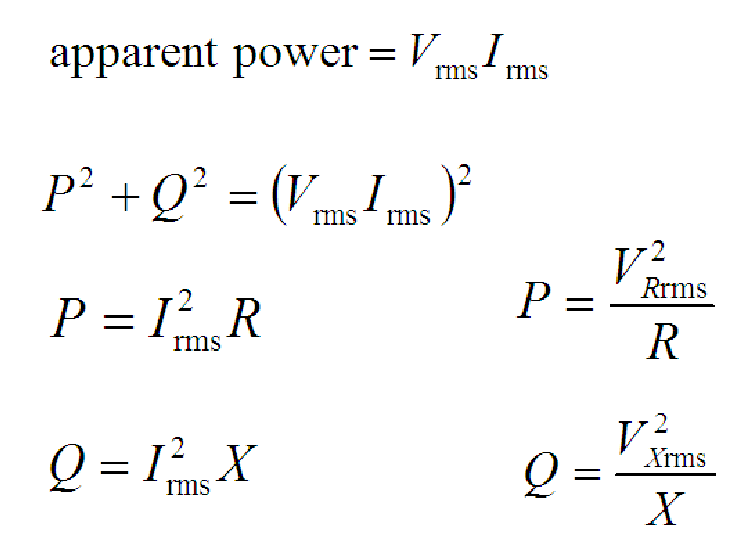
The Future of AC
Guess what? AC’s not slowing down; it’s only getting better! People are going crazy about renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. And you know what? AC is playing a massive role in making these green dreams come true. It’s like the Captain Planet of electricity, saving the planet one watt at a time!
Conclusion
So, there you have it! AC circuits are the real deal, and now you know why they’re cooler than DC circuits. From their dance-like oscillation to the magic of transformers and the power of capacitors and inductors, AC has got it all.
Next time you plug in your charger or switch on the lights, remember the amazing journey that electricity takes to get to you. And if you ever want to impress your friends with your electrical knowledge, just remember – AC circuits are like the rockstars of the electrical world!