What is a Fuel Cell?
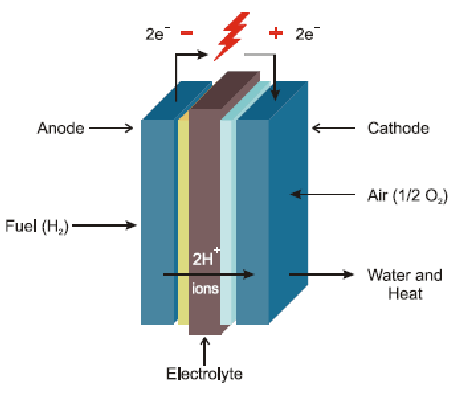
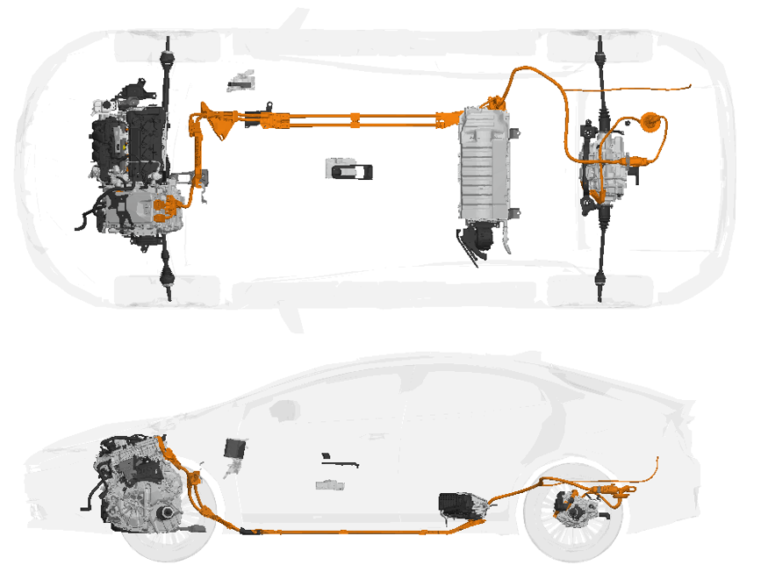
A fuel cell is a device that converts chemical energy directly into electrical energy, water, and heat through electrochemical reactions. It consists of an anode and a cathode separated by an electrolyte, which is typically a porous membrane. Hydrogen, and air (or oxygen) are fed into the cell. At the anode, the fuel undergoes a…