Synthesis of a Copper Coordination Compound & Solubility
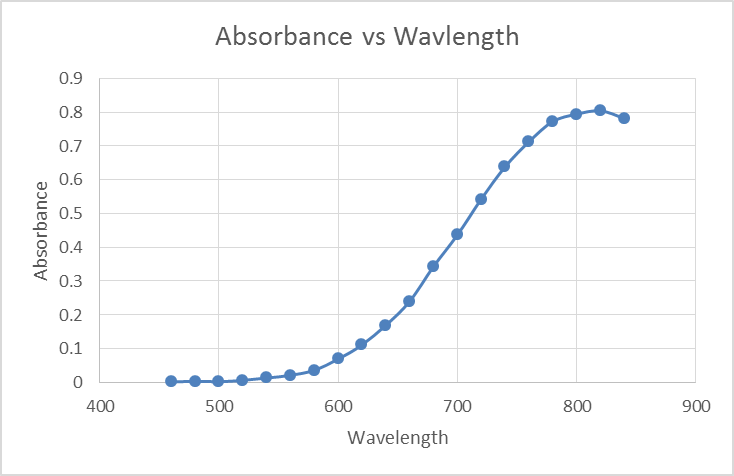
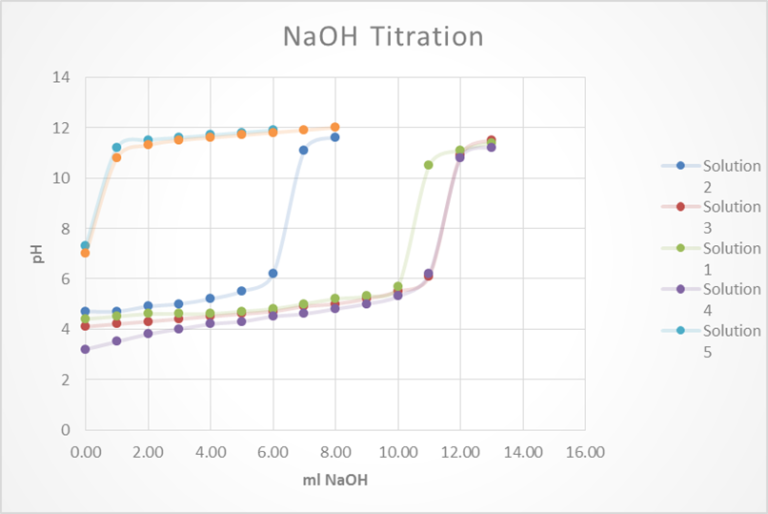
The purpose of this experiment is to prepare a coordination compound of a transition metal, calculate the % yield and then determine the solubility of this compound and solve for Ksp. After conducting this experiment the calculated % yield was 38.2%. The claim is that the experimental Ksp for this compound was 0.0112. For experiment…