Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Security
Abstract
Cyber security attacks are happening now more than ever in computer history. It is estimated that there is a cyber-attack on average every 39 seconds. There exists an overwhelming number of assets organizations need to protect from hackers such as medical information, industrial systems, healthcare devices, and financial information to name a few. With the growing use of Artificial Intelligence, organizations are using this technology to provide another layer into their defense-in-depth approach to mitigate future threats. The purpose of this research is to analyze how Artificial Intelligence strengthens cyber security to protect organizations from data breaches.
Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Security
Everyday new threats are being discovered in the Cyber Security field. It is a constant threat that continues to evolve with new technology as threat actors continue to infiltrate computer networks and systems. The goal of cyber security is to decrease the likelihood of an incident and minimize the impact of an incident while ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the systems and networks. Although policies and procedures are put in place to circumvent incidents from occurring, hundreds of breaches happen each year, with many not finding out until months later. Need arises to study how intelligent security software can help strengthen Cyber Security to protect organizations from data breaches.
When organizations suffer a data breach, it is something that could potentially last them more than expected. Not only do organizations spend a plethora of time and money during the incident itself, this is something that will carry on after the investigation is over. Expenses start to also add up to upgrade the IT infrastructure and train employees. Along with this, organizations deal with having to earn the public’s trust again and tasks like this could include things such as having to pay potentially affected customers with credit monitoring.
According to a study published in 2017 from Centrify, a leading Cyber Security Software company, 65% of data breach victims lost trust in an organization as a result of a data breach. Loss of trust from consumers will cause them to shop with a more secure competitor. Along with loss of customers, organizations could also face fines from governments. In October of 2016, the rideshare company Uber paid Hackers $100,000 if they stayed quiet about the breach and deleted the stolen data. Approximately one year later, Uber finally disclosed the data breach and had to deal with legal issues in many countries such as fines, sanctions, and ultimately loss of customers (Varonis, 2020).
The question of how we can better protect organizations comes up. There are many security protocols put in place throughout organizations all across the globe right now, but hackers still seem to find a way in. One of the fastest emerging technologies right now gaining traction due to higher computational power in modern day computers is Artificial Intelligence. This research will analyze how Artificial Intelligence can be leveraged in Cyber Security for a more secure environment and reduced data breaches.
Problem Statement
Many companies and organizations spend thousands of dollars on hardware and software to secure their infrastructure from cyber threats. While some implement the latest technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, others do not. What they all have in common is that no matter how secure an organization is, there seems to be an increasing number of data breaches all across the globe. The purpose of this research is to analyze how the growth of Artificial Intelligence helps strengthen cyber security to prevent or mitigate data breaches.
Research Question
How does Artificial Intelligence technology compare against current security applications used in IT infrastructures?
Subset Research Question
How can Artificial Intelligence be integrated within already existing applications and infrastructures?
Rationale
In 2015, Cyber Crime damage was reported to be $3 trillion. By 2021, it is estimated that Cyber Crime will surpass $6 trillion annually as reported by an Official Annual Cybercrime Report by Cybersecurity Ventures (2019). Organizations of every size are struggling to keep up with the latest threats from Cyber criminals. Regardless of an organization’s budget, companies from every country are being breached one way or another.
The three most important elements organizations strive to protect are known as the CIA Triad, which is composed of Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. Although organizations follow strict guidelines for defending a network from Cyber Crime, there always seems to be a weak link that allows hackers to gain access to company networks or systems.
While it may be impossible to completely eliminate Cyber Crime, there are multiple steps that organizations do to mitigate the risk. According to The Office of Attorney General Keith Ellison, some common steps organizations use to prevent Cyber Crime include: (1) creating strong passwords, (2) keeping software up to date, (3) only installing trusted applications, (4) and deleting suspicious emails (2020). Most, if not all organizations implement these techniques into their organization’s policies and procedures but still manage to get breached. With new and emerging technology such as Artificial Intelligence, it could provide an edge for companies to further help this crime.
The aftermath of Cyber Crime can be visualized in a domino effect scenario. Not only do organizations suffer from data breaches. The effect goes trickling down to possibly employees. If an organization goes through a data breach and is not fully able to recover from the monetary loss, many employees can potentially lose jobs. Other institutions such as government systems can be breached, which can result in a national security nightmare. According to a Data Connectors Study, Cyber Crime is becoming more profitable than the global trade of illegal drugs (Foster, 2018).
Definitions
The term Cyber Crime describes criminal activities carried out by means of computers or the Internet.
The term defense-in-depth is used as a concept in Information Security in which multiple layers of security controls are placed throughout systems or networks.
The term Artificial Intelligence is broadly used in Computer Science that is the theory and development of computer systems able to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence.
The term CIA Triad is a model designed to guide security policies for information security within an organization.
The term algorithm is a set of rules that precisely defines a sequence of operations.
The term Machine Learning is used to describe a set of computer algorithms that improve automatically through experience.
The term Deep Learning is used to describe a broader family of Machine Learning methods based on Neural Networks.
Hypothesis
Artificial Intelligence can dramatically improve current Cybersecurity technology and impact the number of data breaches organizations suffer through the use of Machine Learning.
H1: Artificial Intelligence significantly impacts the Cyber Security field by mitigating threats.
H2: Artificial Intelligence can be implemented to reduce the workload on Cyber Security professionals through automating tasks.
Literature Review
Technology has been growing at such a fast pace that some systems are having a hard time keeping up with today’s threats in the cyber field. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a tool that can be implemented to help alleviate the growing number of threats we face today. The following review of literature examines Artificial Intelligence from essentially what it is and confirms on why it is important to implement this technology in the cyber field.
The One Hundred Year Study on Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a study based on AI-enabled computing systems. The Study Panel reviewed and documented the potential advances that lie ahead as well as any societal challenges that may arise. From the start, the Study Panel explains how AI is a form of science with computational technologies that has helped many fields such as transportation, healthcare, education, and entertainment. AI helps many fields by learning, reasoning, and taking action – similar to how our nervous system acts. Although many people might see a final product, the Study Panel examines how these impressive AI-enabled technologies typically take years of specialized research and careful, unique construction (Stanford University, 2016).
Shabbir and Anwer (2015) explain the actively and changing world of Artificial Intelligence (AI), which has a long history. Many of today’s modern AI systems have the ability to learn and quickly adapt as to how they can be restructured to vastly improve their performance. AI tools can vary depending on the application but some of the most common used include machine learning, deep learning, and predictive analysis. The authors go on to explain how human intelligence can differ from artificial intelligence in modern day computing systems and the challenges AI has to reach and outperform human intelligence.
Artificial Intelligence is a technology under scrutiny due to society thinking that it can vastly impact the labor market by reducing workers by automating many of today’s tasks. Automation technologies do have the potential to disrupt a significant portion of all occupations, at least to some degree. The authors brought to the reader’s attention that there is much more than just automating tasks. For AI to significantly make an impact in today’s labor market, there needs to exist high-quality data relevant to every specific industry needing automation. This creates a true barrier to overcome when building high quality Artificial Intelligence applications (Schinkman, 2019).
Kowalski (2016) examines various processes on how Artificial Intelligence (AI) is able to come up with certain decisions based on the input it has received. Such techniques for different applications include formal logic, probability theory, management science, linguistics and philosophy. One of the most powerful techniques also include computational logic. Computational logic builds upon the traditional logic and the classic decision theory technique, which results in a method that can not only be used effectively in computing systems but also in our daily ordinary life to rationalize our decisions we make without the involvement of a computer.
Nuffeld Council on Bioethics examined Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare research. Due to the information age we currently live in, the field has been rapidly advancing due to the amount of digital data at our disposal. Many high-profile corporations such as Microsoft, IBM, and Google have been heavily investing in AI technologies for various fields. Although large amounts of data exist, some fields have a hard time using such data due to the quality of the data. This is an issue due to a shortage of quality data that can result in the inability to display some human characteristics. For example, Banner (2018) explains that due to the lack of quality data, it can result in ethical issues if an AI system has to make an important decision and is basing it on the amount or quality of the data it currently has available.
Ann Geisel (2018) in The Current and Future Impact of AI on Business reviews how there are several layers and types of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that can be implemented into the business world. Implementing AI into many forms of businesses can create a better world for humanity. Geisel explains that many businesses can use a type of AI that has limited learning capabilities, which essentially means that there will not be a need to fear potential job loss to humans or danger to the human life. Such systems implemented can be included in marketing, sales, accounting, finance, and computer systems.
Dr. Pranav Patil (2018), examines how Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be and should be used when applying logic in Cyber Security applications. Much of today’s software is programmed with a standard mounted algorithm, which in many cases is perfectly fine depending on the use of the application. On the other hand, hard wiring the logic to a program will result in the decision process practically being very stale and not intelligent enough for more sophisticated applications that require it. For example, in the Cyber Security field, it is best to not hard-wire logics (algorithms) on deciding what to do because of the dynamically evolving attacks on networks.
Newman (2019) in Towards AI Security details in her published article a specific framework on how to navigate the complex landscape of AI security not only in the United States but across the globe. Due to the recent demand in Cyber Security and the merger with Artificial Intelligence, there are significant policy gaps that policy makers around the globe should take into account. The reason for this is because AI is one of the most important global issues of the 21st century. Due to the security implications, we have today, it can dramatically alter how we shape our future experiences.
There is a major global impact cyber-attacks have on economies worldwide. Cyber threats will continue to rise as long as we have interconnected devices and attackers have a motive to continue the attacks. Artificial Intelligence can help alleviate these threats by implementing the technology into the cyber field. However, further research is needed to more clearly categorize the difficulties Artificial Intelligence has on the decision-making process based on the current information the system has at its disposal.
Methodology
The research methodology used for this research paper included the exploratory research methodology. Exploratory research is a type of research that is conducted in an area of study that has not clearly been finalized (Lewis, 2012). In other words, research is conducted so that the researcher can provide further understanding about that particular problem that is not clearly defined. The reason this research methodology is appropriate for this research is because the mix of Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Security related applications is fairly new in the industry within the last couple of years. According to the University of Washington, Artificial Intelligence (AI) was first coined by John McCarthy in 1956 (Smith, 2006). AI has a long history of research conducted but has not been thoroughly research in Cyber Security due to the need for it until recent years. The term Cyber Security was originally patented by MIT in 1983 (Matthew, 2019). Due to the lack of internet connections worldwide at the time, the need for Cyber Security professionals was miniscule. Fast forward to present day, with nearly 1.9 billion websites and 4 billion internet users, cybercrime is expected to cost the world in excess of $6 trillion annually by 2021, up from $3 trillion in 2015 (Herjavec Group, 2019).
The procedure that I used to conduct this research is by thoroughly reviewing current journals already published on cybersecurity and artificial intelligence. I analyzed and processed the collected data in a research manner that allowed me to categorize Cyber Security related attacks depending on the solutions used during those breaches. For example, data currently exists on breaches and that data will be used to compare what technologies were already in place before the breach occurred. In 2019 alone, according to Norton Inc., there were 3,800 publicly disclosed security breaches with a massive 4.1 billion records exposed (Rafter. 2019). Along with this information, it was used to analyze how Artificial Intelligence is gaining traction within the industry and to provide further intelligence on where those Artificial Intelligence applications stand in the industry.
In summary, Cyber Security and Artificial Intelligence are both widely growing industries that can benefit from one another. Although both fields go back more than 30 years since their start, there is still much to learn and improve, which creates a vast amount of opportunities more many people to study and learn from.
Results
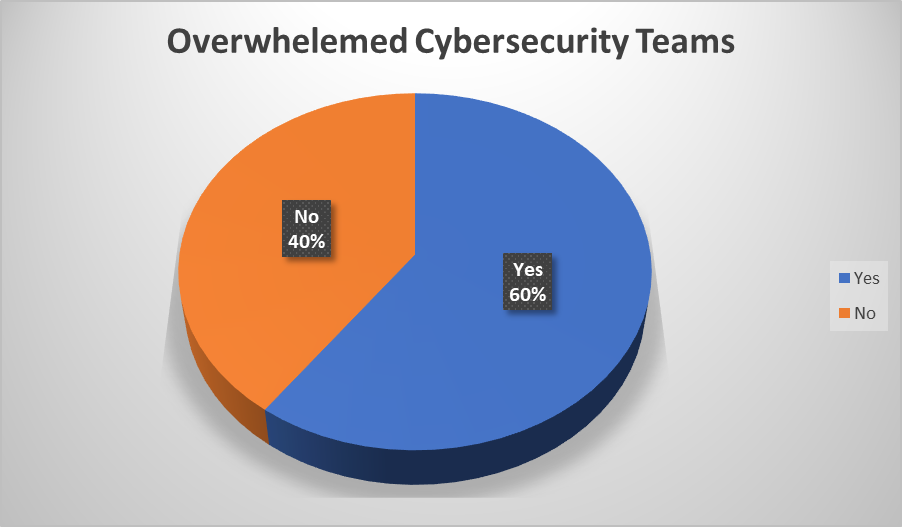
There was significant effect on data breaches for those who did not use Artificial Intelligence (AI) as opposed to those organizations who had AI implemented. According to press releases from those companies who had data breaches, cybersecurity analyst find it very difficult to effectively monitor vast amounts of data volumes produced from various log outputs. An independent research conducted by Security Firm Capgemini interviewed over 850 firms, which resulted in 60% saying that their cybersecurity teams are overwhelmed (Figure 1). An overwhelmed team focuses most of their resources on going through data
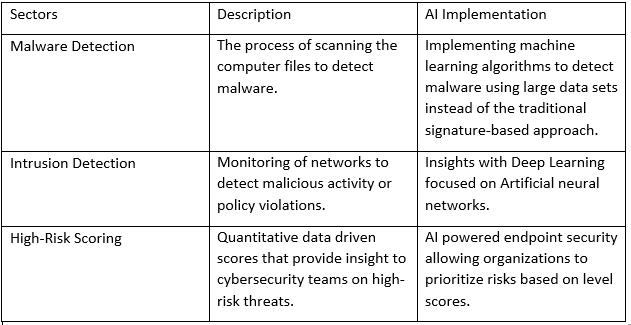
Three main cases were analyzed in accordance on how AI significantly impacts these sectors, which include: (1) Malware Detection, (2) Intrusion Detection, and (3) High-Risk Scoring. Table 1 shows the correlation between the three sectors and how AI improves them to better protect against data breaches.
Table 2 AI Cybersecurity detection correlation.
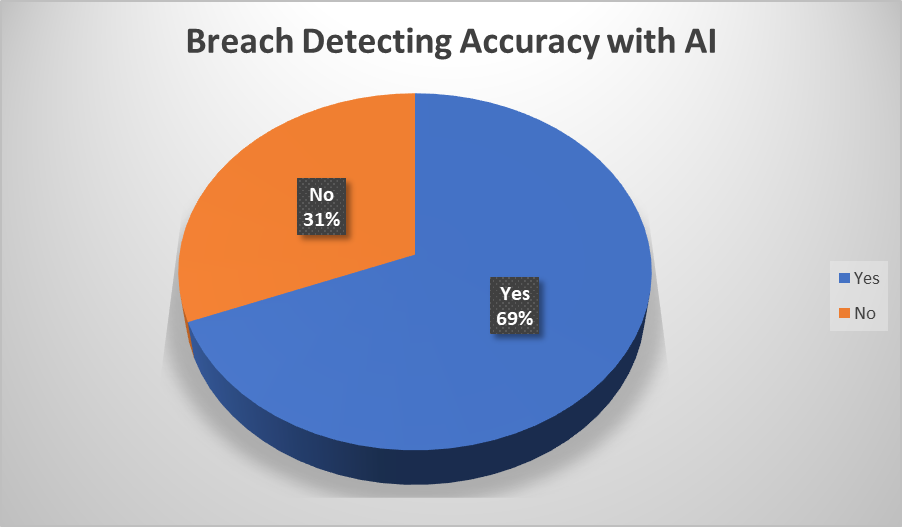
Artificial Intelligence drastically improves the cybersecurity team’s bandwidth. AI algorithms have the capability to process data faster than humans, which takes the log monitoring workload off the cybersecurity team. With Artificial Intelligence, detected threats are reduced by up to 12%, resulting in less data breaches and higher accuracy to detect breaches (Figure 2). Also, by using AI algorithms to process data in record time, threat actors that remain undetected drop by 11%.
Discussion
The findings from the study suggest that using Artificial Intelligence in cybersecurity vastly strengthens organizations by quickly identifying possible threats before an actual data breach occurs. The reason for this is because Artificial Intelligence is a technique that enables a machine to mimic human behavior at a larger scale with vast amounts of processing power.
There was no evidence that statistically proved Artificial Intelligence would be able to completely eliminate security breaches. Nonetheless, there was significant evidence trend that resulted in multiple instances where Artificial Intelligence would crucially reduce man hours on total time spent analyzing data log incidents for activities such as malware and intrusion detection.
The technology behind the power used in Artificial Intelligence is within Machine Learning. Machine Learning are algorithms that give the ability for computer systems to learn from data and make predictions based on the data received. Machine Learning is useful in many applications where a specific data set is given to an algorithm to differentiate between two anomalies. Specifically, Cyber Security threats are changing every day and systems need more than Machine Learning to find new anomalies not known by previous signatures. A subset of Machine Learning that allows for this problem to be solved is by using Deep Learning.
Deep Learning uses a type of Artificial Neural Network that takes metadata as input and processes that data through an algorithm of layers to optimize detection of anomalies. However, this type of Deep Learning algorithm only works well with large amounts of data so that systems can thoroughly understand threats and reduce False Positives and False Negatives.
Deep Learning integrated within Cyber Security applications allows for organizations to collect and aggregate logs of data and feed this into the Neural Network Algorithms. Not only will a system integrated with Deep Learning be able to detect unwanted activities, it can also perform root cause analysis. The algorithm processes through all the data collected within seconds, something that can take a human hours or days to analyze. By using this technique, the organization is able to implement a highly effective process that becomes proactive to detect anomalies and strange patterns before the systems or networks start to become unavailable or infected.
An organization to fully benefit from Neural Network technology would need to have in place other systems that can feed the algorithm large data sets from sources such as network sensors, CRM’s, server logs, or application logs. It is possible to implement a Neural Network with limited data sets, but organizations would face the possibility of creating more False Positives and False Negatives in alerts.
Conclusion
In Conclusion, the study was conducted dealing with the impact Artificial Intelligence (AI) has on Cyber Security applications in relation to data breaches. The research was conducted on a case-by-case study with open-source publications from companies that suffered data breaches. Over half of the publications showed that their Cyber Security teams were overwhelmed with the amount of data they must review as opposed to those using AI as a supplemental resource. As a result, these indications show significant evidence that Cyber Security teams are focused more on past events as opposed to monitoring the networks in real time. From these findings, we can start to see how Cyber Security teams being backlogged with vast amounts of data correlates with data breaches being discovered weeks or months after the incident had occurred. Overall, this study suggests that Artificial Intelligence significantly plays a vital role in the defense in depth strategy for organizations to mitigate data breaches.
References
- AAG Services. (2019, September 18). How often do Cyber Attacks occur? – AAG – Managed IT Solutions. Retrieved from https://aag-it.com/how-often-do-cyber-attacks-occur/
- Banner, N. (2018). Artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare and research. Retrieved from https://www.nuffieldbioethics.org/wp-content/uploads/Artificial-Intelligence-AI-in-healthcare-and-research.pdf
- Capgemini. (2019, July). Reinventing Cybersecurity with Artificial Intelligence. Retrieved from https://www.capgemini.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/AI-in-Cybersecurity_Report_20190711_V06.pdf
- Centrify. (2017, May). The Impact of Data Breaches on Reputation. Retrieved from https://www.centrify.com/media/4772757/ponemon_data_breach_impact_study_uk.pdf
- CyberSecurity Ventures. (2019, September 19). Global Cybercrime Damages Predicted To Reach $6 Trillion Annually By 2021. Retrieved from https://cybersecurityventures.com/cybercrime-damages-6-trillion-by-2021/
- Foster, J. (2018). Data Connectors: 21 Terrifying Cyber Crime Statistics. Retrieved from https://www.dataconnectors.com/technews/21-terrifying-cyber-crime-statistics/
- Geisel, A. (2018, May). The Current And Future Impact Of Artificial Intelligence On Business. . Retrieved from https://www.ijstr.org/final-print/may2018/The-Current-And-Future-Impact-Of-Artificial-Intelligence-On-Business.pdf
- Kowalski, R. (2016). Artificial Intelligence and Human Thinking. . Retrieved from https://www.ijcai.org/Proceedings/11/Papers/013.pdf
- NEWMAN, J. (2019). Toward AI Security. Retrieved from https://cltc.berkeley.edu/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/CLTC_Cussins_Toward_AI_Security.pdf
- Patil, P. (2018). ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE IN CYBER SECURITY. Retrieved from https://www.academia.edu/25349174/ARTIFICIAL_INTELLIGENCE_IN_CYBER_SECURITY
- Scheinkman, J. (2019, January). Toward understanding the impact of artificial intelligence on labor. Retrieved from http://ide.mit.edu/sites/default/files/publications/1900949116.full AI.pdf
- Shabbir, J., & Anwer, T. (2015, August). Artificial Intelligence and its Role in Near Future. Retrieved from https://arxiv.org/pdf/1804.01396.pdf
- Standford University. (2016). ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND LIFE IN 2030. Retrieved from https://ai100.stanford.edu/sites/g/files/sbiybj9861/f/ai_100_report_0906fnlc_single.pdf
- The Office of Minnesota Attorney General . (2020). Internet Safety: How to Protect Yourself Against Hackers. Retrieved from https://www.ag.state.mn.us/Consumer/Publications/HowtoProtectYourselfAgainstHackers.asp
- Varonis. (2020, March 30). Analyzing Company Reputation After a Data Breach: Varonis. Retrieved from https://www.varonis.com/blog/company-reputation-after-a-data-breach/