Understanding a Supercapacitor
A supercapacitor is an advanced energy storage device that offers high power density and has a long cycle life. These devices store energy through the separation of charge in an electrolyte, rather than through the chemical reactions used in batteries. This technology has undergone extensive developments in the last few years. Positioned between batteries and dielectric capacitors on the energy-power spectrum, supercapacitors offer higher power densities than dielectric capacitors and higher energy densities than batteries.
What is the working principle of a supercapacitor?
SupercapacitorsIt are a type of capacitor with a high capacitance value, significantly exceeding that of solid-state capacitors but with lower voltage limits. This type of capacitor serves as a link between electrolytic capacitors and rechargeable batteries. Ultracapacitors are commonly used in applications where rapid energy storage and release are required, such as regenerative braking systems in vehicles and power backup systems.
What are supercapacitors also known as?
A supercapacitor, also known as ultracapacitors (often associated with the brand name Maxwell), or electric double-layer capacitors (EDLCs).

How does a supercapacitor work?
An EDLC operates through the reversible adsorption of ions from an electrolyte onto stable active surfaces. This process occurs on high surface area electrodes made possible by nanoparticles. By tailoring the pore sizes of these electrodes, ultracapacitors can achieve maximal normalized capacitance, enabling them to store and release large amounts of energy efficiently. This design allows supercapacitors to deliver high power density and long cycle life, making them valuable for applications requiring rapid energy storage and release.
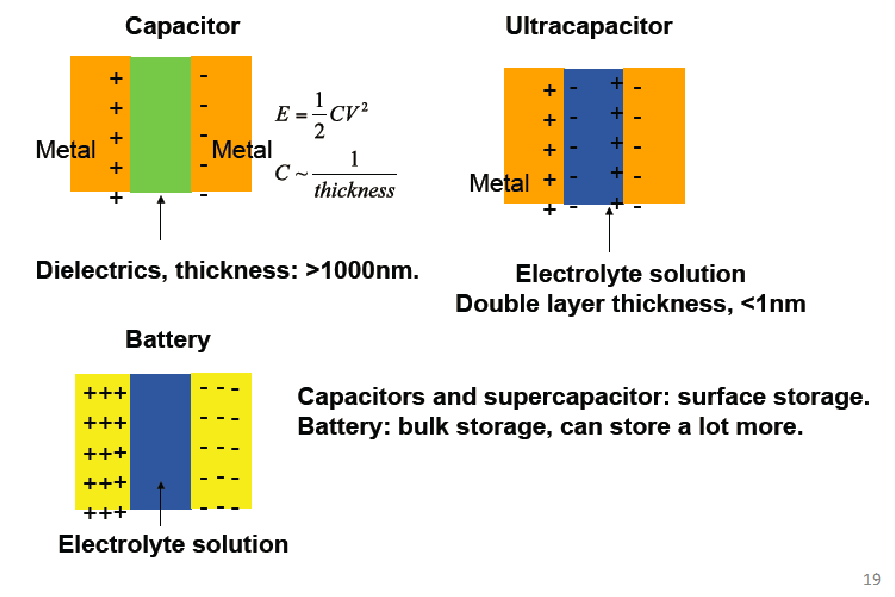
Supercapacitor vs a Capacitor
When comparing D-cell-sized capacitors, an aluminum electrolytic capacitor of this size, typically coated with Al2O3, may have a capacitance approaching 0.28 farads (F), calculated as 37 cubic centimeters multiplied by 7500 microfarads per cubic centimeter. In contrast, a supercapacitor of a similar size boasts a much higher capacitance, ranging from 310 F to 350 F. This significant difference in capacitance highlights the superior energy storage capabilities of ultracapacitors compared to traditional aluminum electrolytic capacitors.
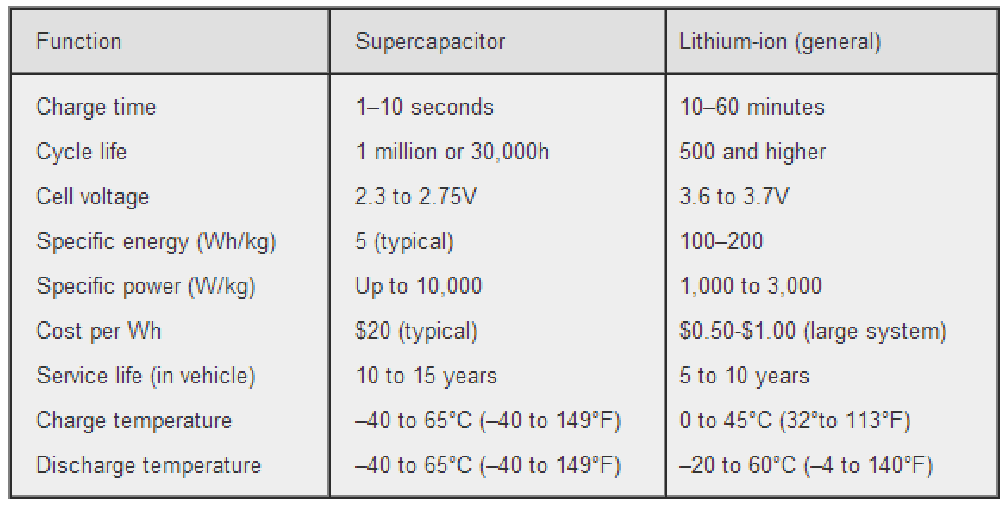
Supercapacitor vs a Battery
The construction of a supercapacitor is similar to that of a battery, with some key differences. Like a battery, it consists of porous electrodes with a high surface area and a separator. However, unlike a battery, the electrodes in a supercapacitor are chemically symmetrical.
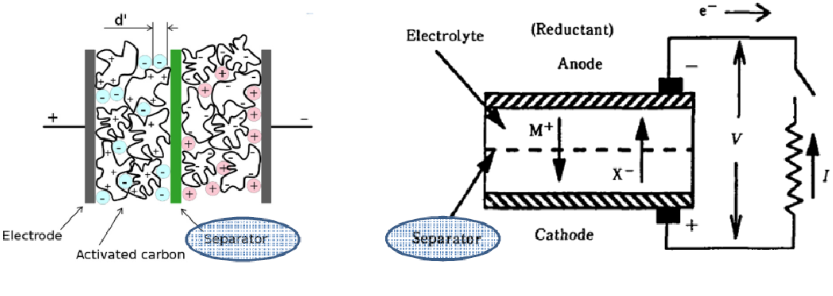
This means that both electrodes have the same material composition, which allows for faster ion movement and higher power density. The symmetrical nature of the electrodes also contributes to the long cycle life of ultracapacitors, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent charge and discharge cycles.
What are the advantages of supercapacitors compared with batteries?
A supercapacitor offers several advantages over traditional batteries. These include high capacitance per unit volume (approximately 1200 times that of aluminum electrolytic capacitors), a fast charge and discharge rate (around 300 times that of batteries), which is beneficial for integrated designs, and an ability to enhance the power and cycle life of battery systems. Due to their unique construction ultracapacitors are also more efficient than batteries, especially under full loading conditions.
Why don’t we use supercapacitors instead of batteries?
Capacitors have the ability to store energy temporarily, but they lack the energy density of batteries, making them unsuitable for long-term energy storage or providing a continuous power supply.
Energy vs. Power
Ultracapacitors serve as a bridge between batteries and conventional capacitors, offering a unique combination of characteristics. They can achieve greater energy densities compared to conventional capacitors while maintaining the high power density typical of capacitors.
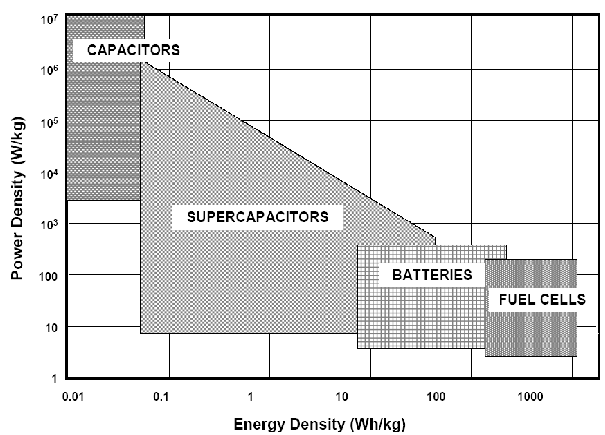
This dual capability makes ultracapacitors a potentially versatile solution for a variety of emerging energy applications. Their ability to achieve a wide range of energy and power density levels makes them attractive for use in applications where high power output and rapid energy discharge are crucial, such as in electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and portable electronics.
Good applications for supercapacitors
Supercapacitors find excellent applications in various fields due to their unique characteristics. For
hybrid electric buses, where a long lifetime is desired. Another application of ultracapacitors is in
aircraft, doors actuators. In hybrid electric vehicles, they can provide emergency brake power, ensuring
safety in critical situations. Additionally, ultracapacitors are used for DC bus voltage stabilizations.
Finally, another application of ultracapacitors includes photocopier startup.
Conclusion
In conclusion, supercapacitors represent a fascinating and rapidly evolving technology in the realm of energy storage. Their unique ability to deliver high power densities and long cycle lives, coupled with their fast charging and discharging capabilities, make them ideal for a wide range of applications, from portable electronics to electric vehicles and renewable energy systems. As research and development in this field continue to progress, it is clear that supercapacitors will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of energy storage and consumption, paving the way for more efficient and sustainable technologies.