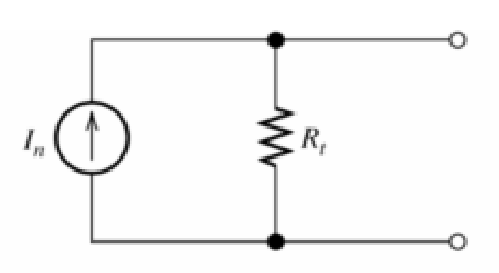
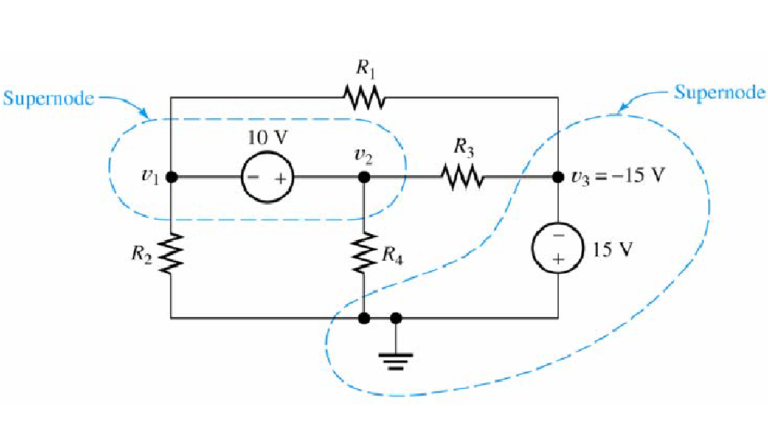
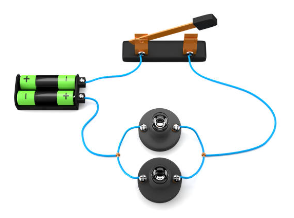
Unlocking the Power of Inductors
When an electrical current flows through a wire, the current generates a small magnetic field around the wire. If the wire is shaped into a coil, the magnetic field becomes much stronger, thus an inductor is created. Today we’re going to dive into the world of inductors and see how these amazing devices shape the…