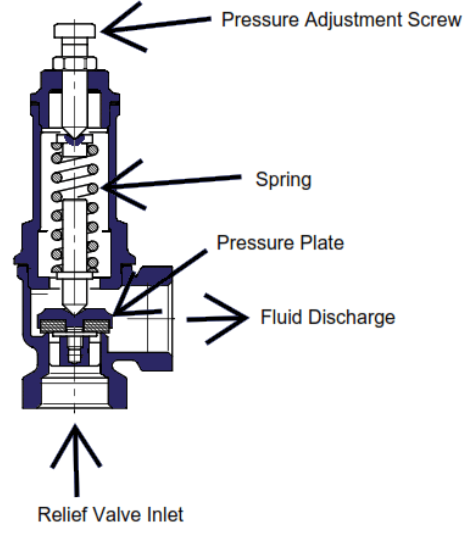
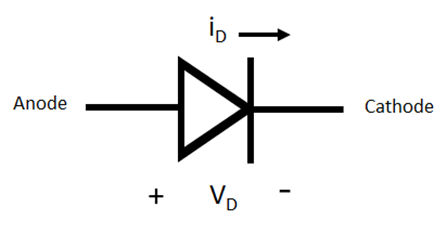
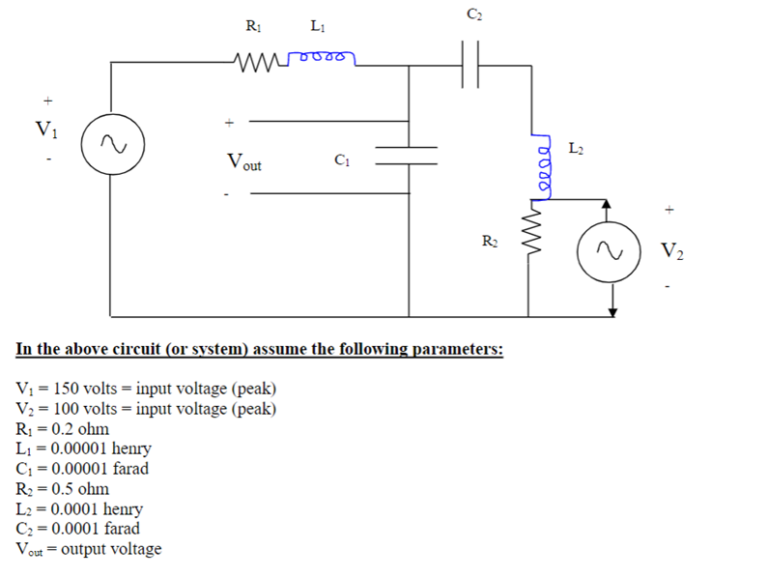
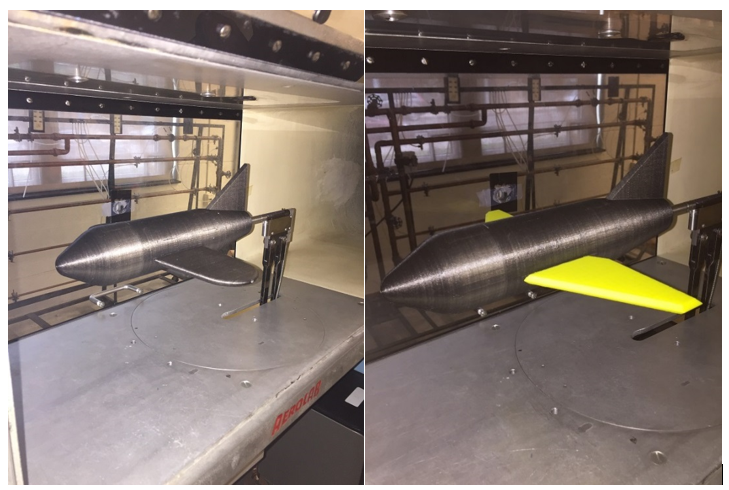
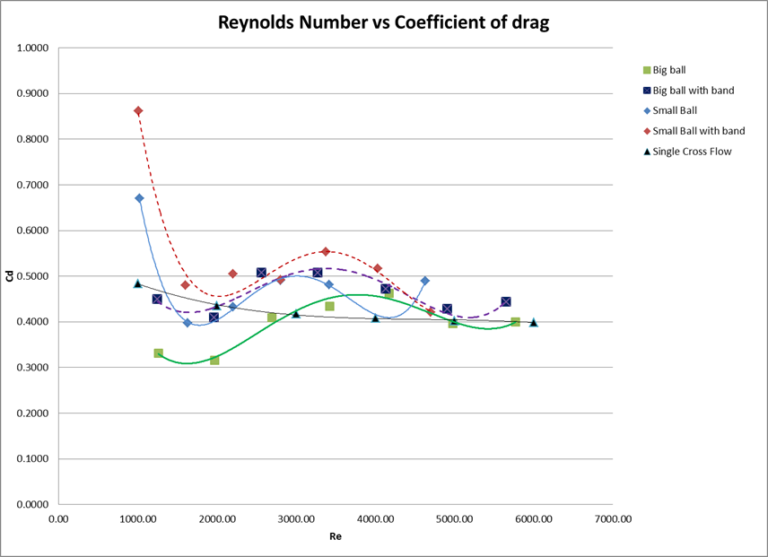
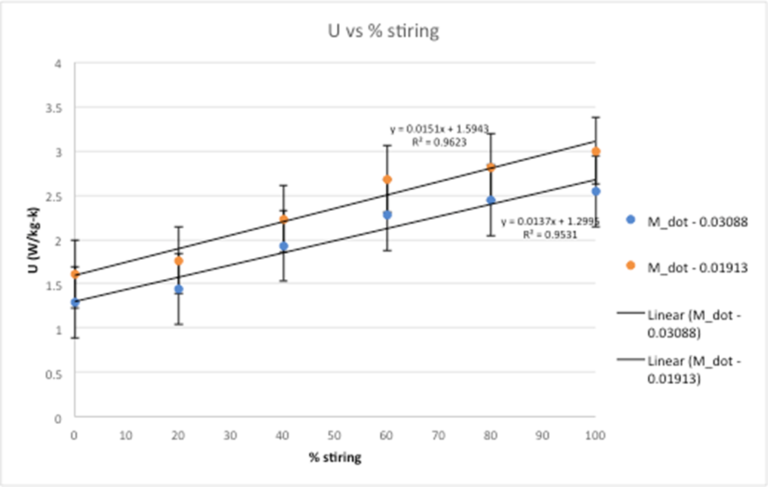
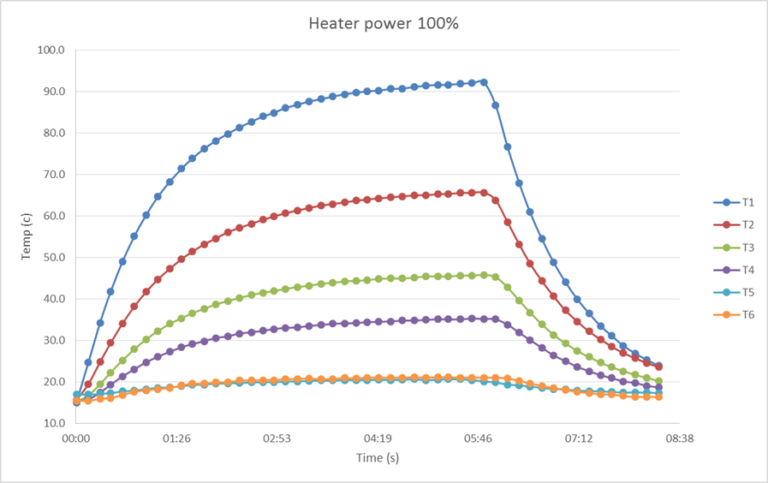
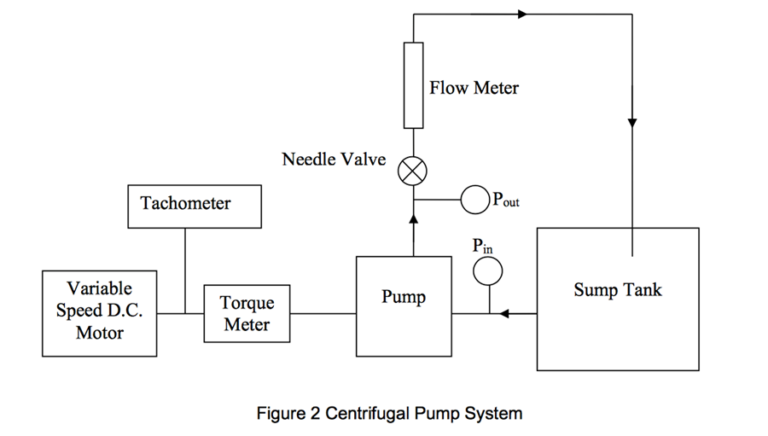
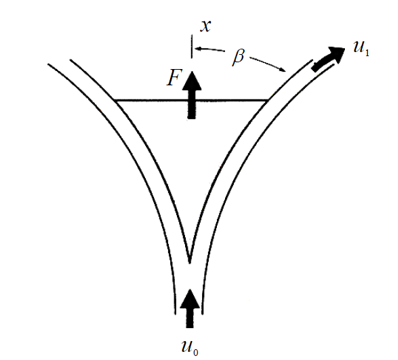
The Relief Valve
The relief valve is designed or adjusted to open at a specific set pressure, ensuring that pressure vessels and other equipment are not exposed to pressures exceeding their intended limits, thus protecting them. Pressure relief valves are commonly used in hydraulic systems, but they frequently fail under harsh conditions. To ensure the dependable operation of…