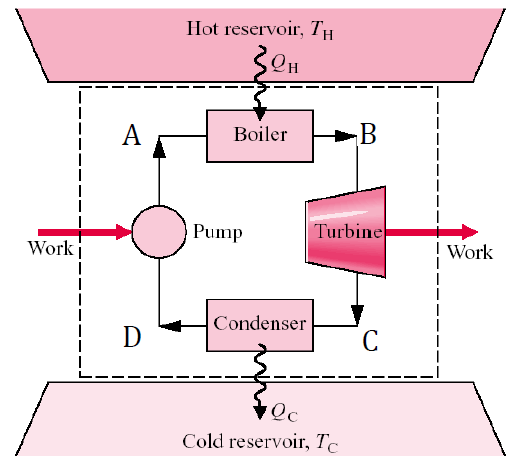
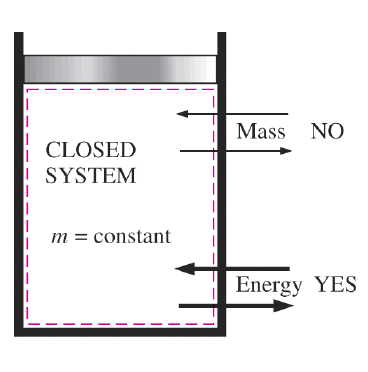
Understanding Availability and Exergy in Thermodynamics
In the world of thermodynamics, analyzing energy alone is not enough to fully understand how systems perform or how efficiently they operate. While energy is conserved, not all energy is equally useful, this is where the concepts of availability and exergy come into play. These two ideas provide insight into the quality of energy and…