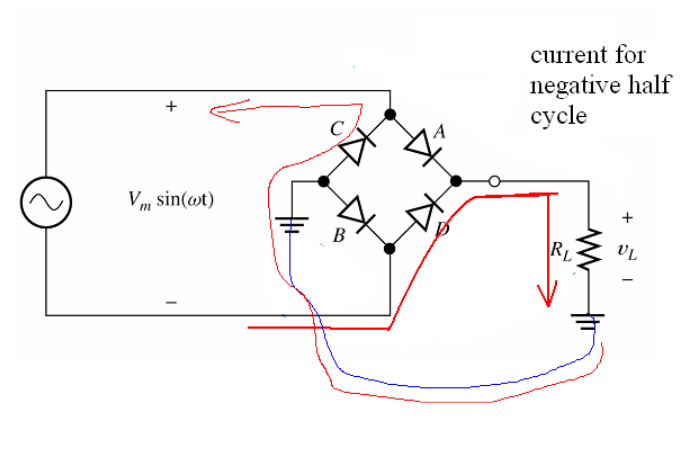
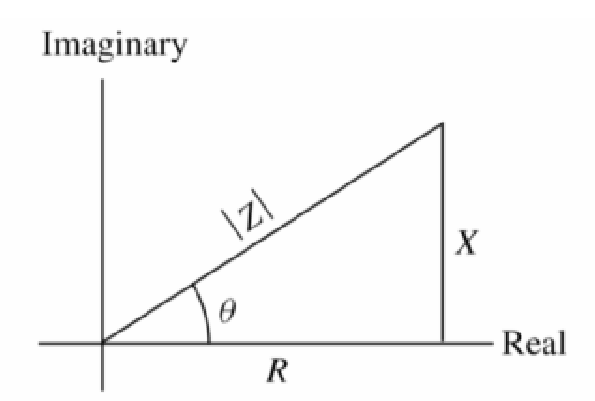
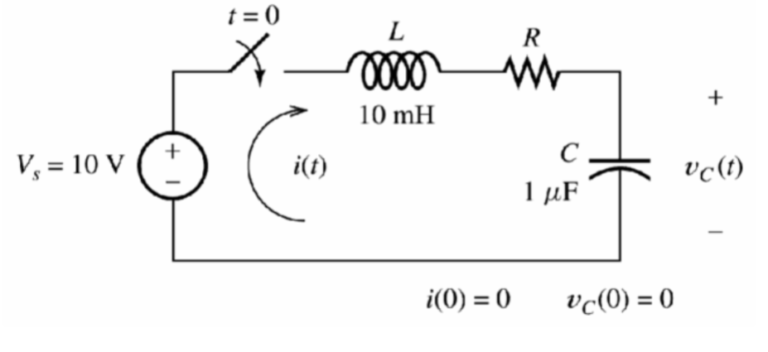
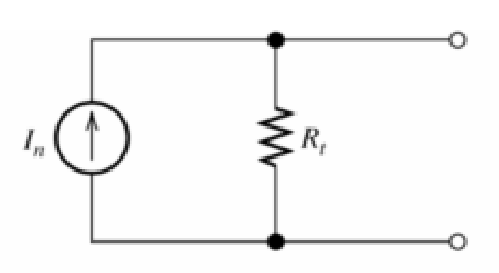
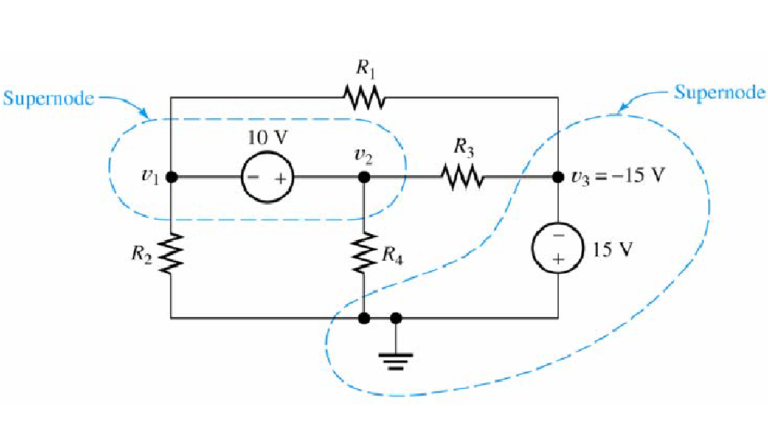
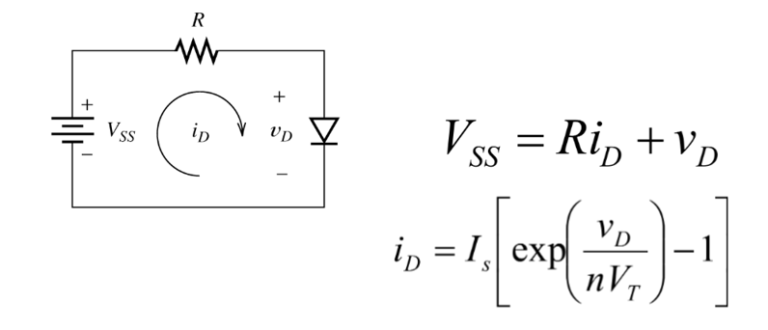Rectifier Basics
Many electronic circuits require DC voltage to operate, but the voltage from a standard 120V outlet is AC. A rectifier provides an easy way to convert AC voltage or current into DC voltage or current using a diode. A p-n junction diode allows electric current to flow in one direction (forward bias). By blocking current…