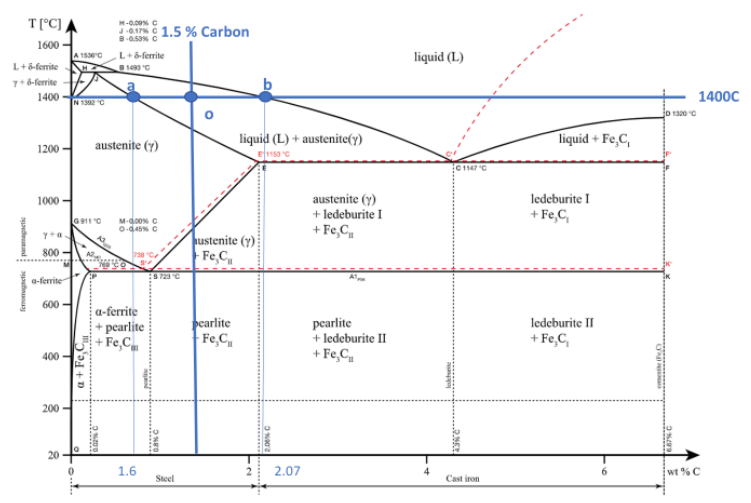
Determining Material based on Mechanical Properties
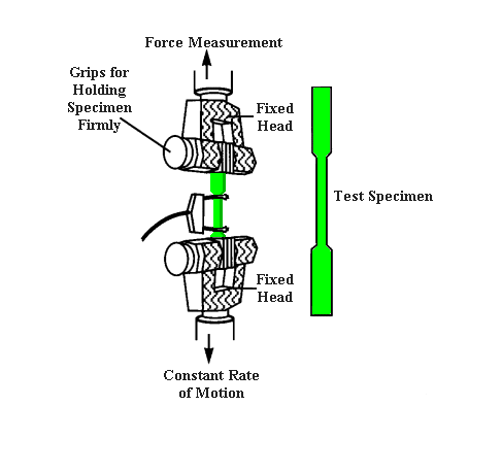
Objective The object of the experiment is to determine the material of an unknown specimen based on the material young’s modulus(E). Young’s modulus is the ratio of the stress to strain in the plastic region of the stress-strain diagram. This mechanical property is material specific. The data which was gathered during this experiment is as…