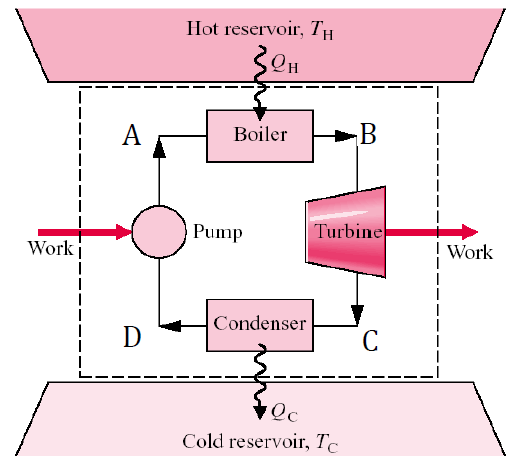
Understanding Thermodynamic Cycles
Thermodynamic cycles are fundamental principles in engineering, establishing the basis for the operation of power plants, internal combustion engines, refrigerators, and air conditioners. These cycles describe the processes a working fluid undergoes to convert heat into work or vice versa. This article explores various thermodynamic cycles, including basic, Carnot, Rankine, Otto, Diesel, Brayton, refrigeration, and…