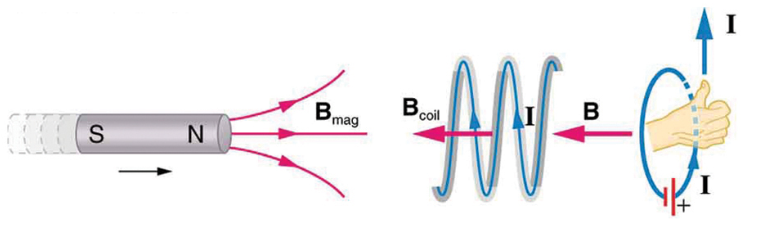
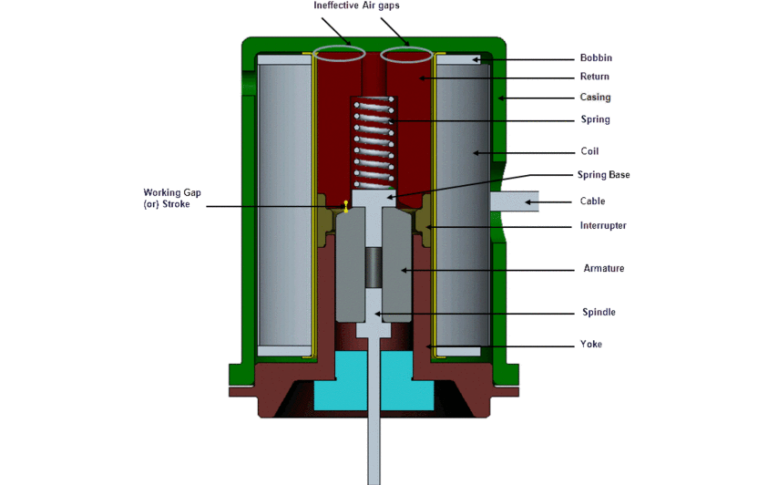
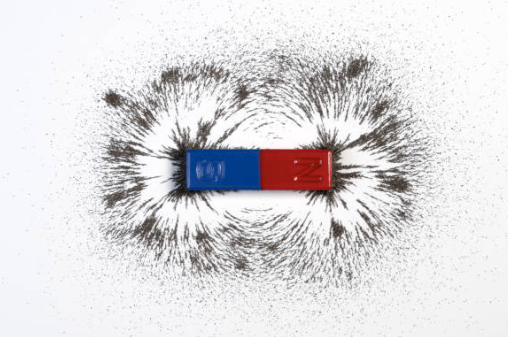
Understanding Optical Instruments and Interference
Optics is a fascinating field of physics that deals with the behavior of light and its interactions with different media. This article explores key concepts in optical instruments, interference, and thin-film applications. Magnifiers and Angular Magnification A magnifier, such as a magnifying glass, enhances magnification by increasing an object’s apparent angular size as seen by…